Disaster Prevention

Disaster Prevention with Professional Response
Factors affecting the safety of THSR trains can be divided into three categories, including: natural factors, human factors and equipment abnormality (see the table below). In accordance with the overall prevention and contingency plan for the three categories of disasters, the Company puts the safety of passengers and personnel first, formulates emergency procedures to respond to actual disasters, and takes various measures to improve and resume operations through cooperation between internal and external units.
Emergency Response Flow Chart for Various Disasters
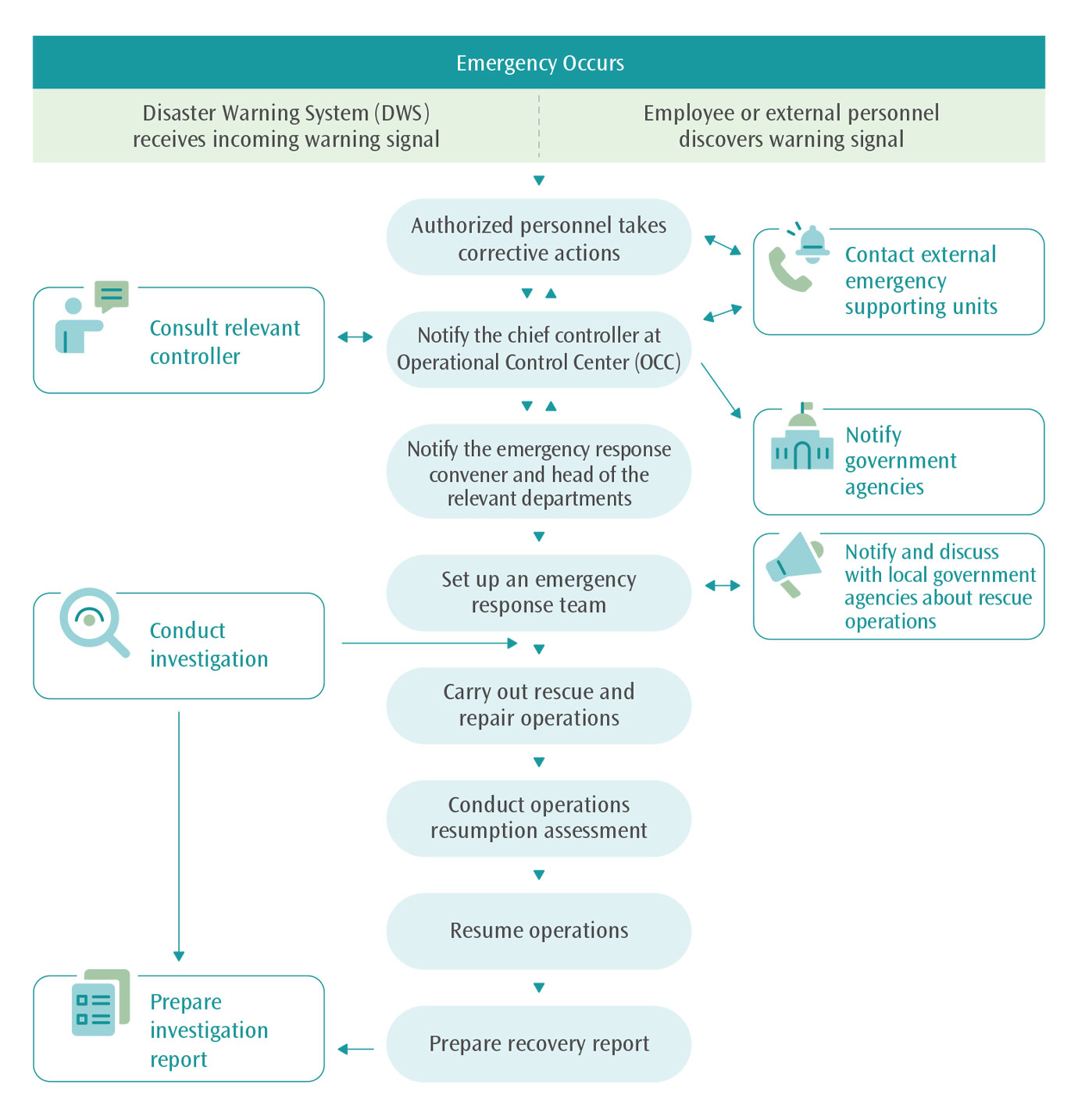
THSRC has adopted relevant laws and regulations on disaster prevention and fire safety as the basis for the formulation of internal plans and measures, and each station or depot implements various disaster prevention tasks as per the internal plans. The standard operating procedures for disaster response are also independently inspected for safety by international experts in the final inspection phase to ensure that the procedures can cope with various potential disasters that affect transportation safety. All operating procedures are regularly inspected and revised in accordance with regulations, and all inspection operations are completed according to the frequency of inspection during the epidemic period in compliance with epidemic prevention regulations to ensure the reliability of equipment. The relevant disaster or emergency response operation rules and procedures of each unit shall be reviewed at least once every three years, and the effectiveness shall be periodically reviewed through legal compliance operations every quarter, the relevant emergency response procedures shall be continuously improved at each emergency response operation review.
Natural Disaster Prevention Measures
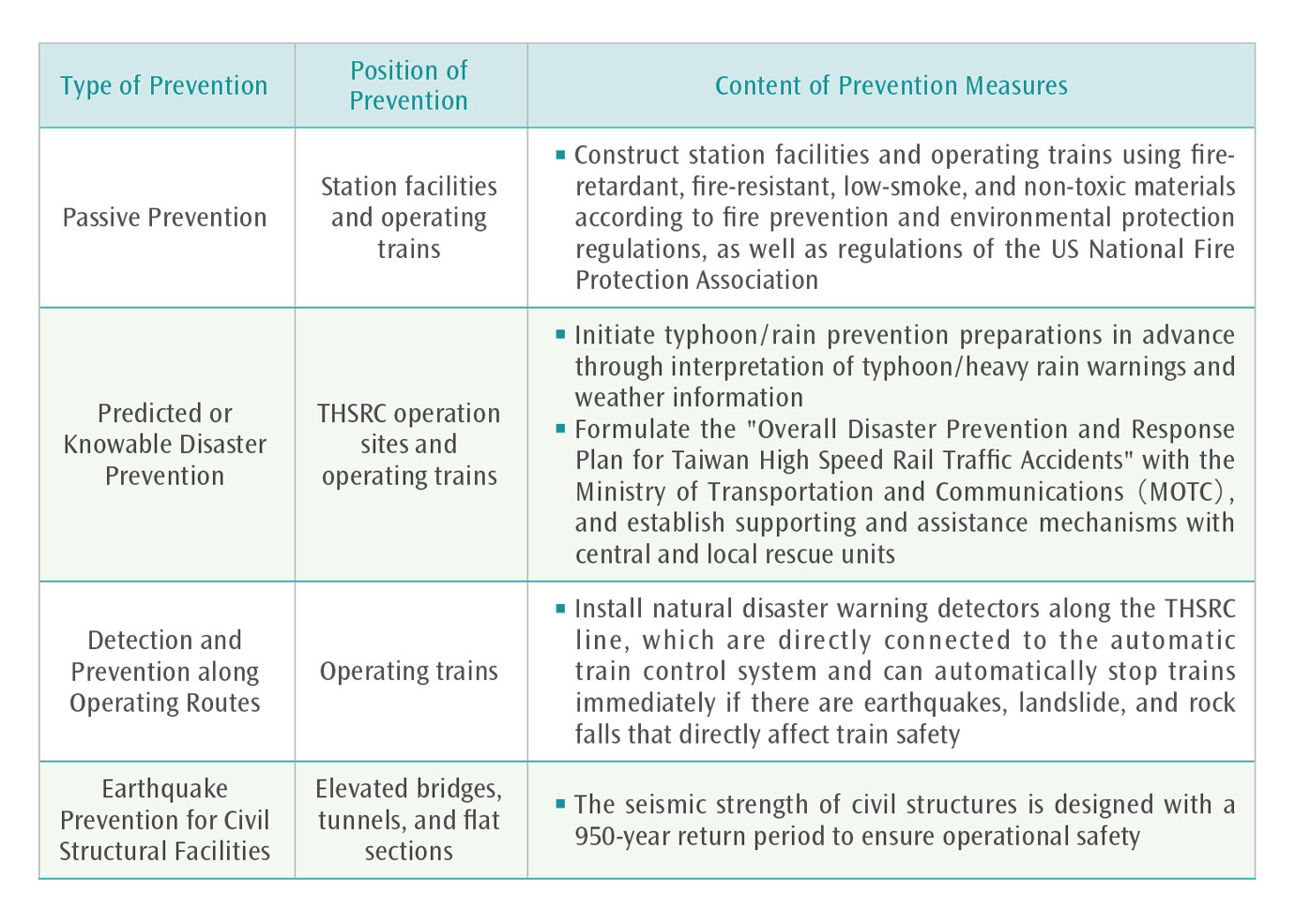
THSRC's trains are equipped with Disaster Warning System(DWS), if earthquakes, rockfalls, landslide, road vehicle intrusion and other safety-related danger signals are detected, the automatic train control system will be triggered to send a stop command to stop the train. Intrusion Sensor include three types of sensors, including rockfall, landslide and road vehicle intrusion, which are installed on road sections with higher risk according to the characteristics, such as a total of 28 road vehicle intrusion detectors were set up above the tunnel portal or on the viaduct with high risk of vehicle intrusion. In 2024, THSRC completed the three-year repair project of the disaster warning system to ensure the stability and reliability of the system, and there were no train delay caused by abnormal intrusion detector. In the Hualien earthquake that occurred in April 2024, the DWS immediately suspended the operation and activated the emergency response measures after detecting the earthquake warning, and coordinated with each unit through the operation control center to complete the emergency response and safety inspection within 5 hours and resume according to the schedule.
DWS Framework
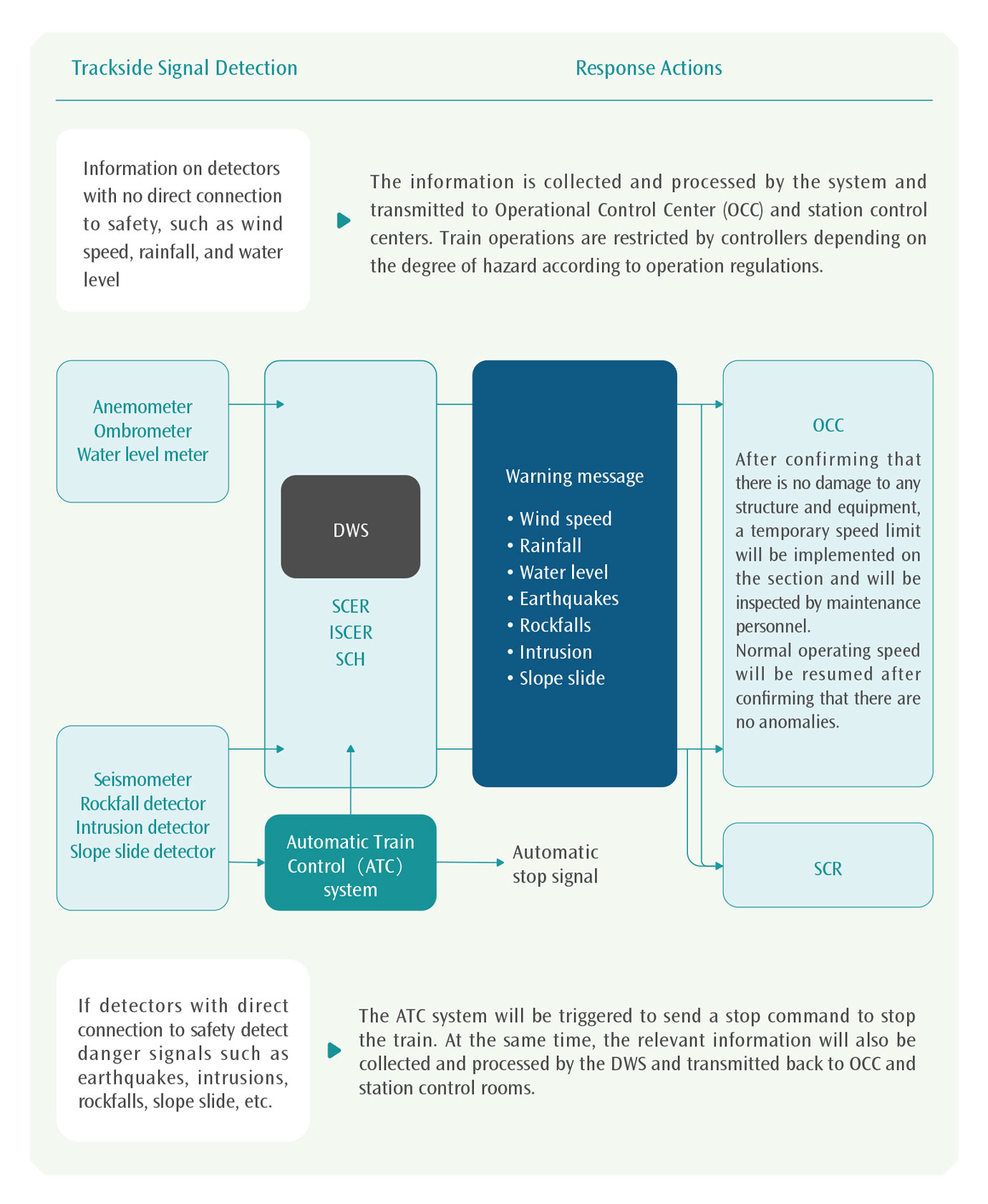
Notes:
1. SCER: Signaling and Communication Equipment Room
2. ISCER: Intermediate Signaling and Communication Equipment Room
3. SCR: Station Control Room
4. SCH: Signaling and Communication Hut
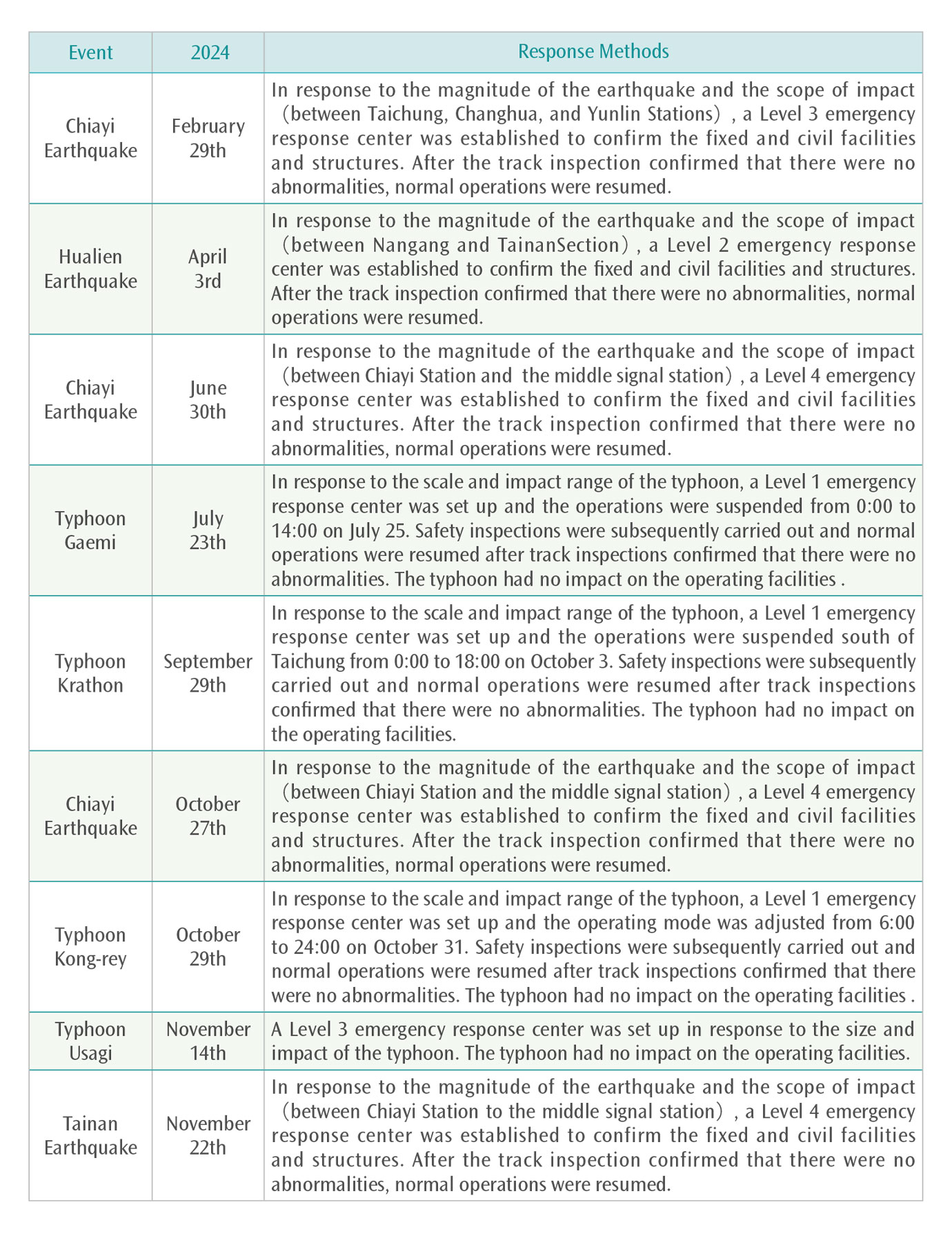
Relevant information on the actual natural disaster events affecting the THSRC operation in 2024 is as follows:
Disaster Events Affecting Operations
As for man-made disasters, THSRC not only develops a "Material Man-Made Security Incident or Terrorist Attack Contingency Plan" to facilitate coordination with government agencies and to set up operational mechanisms, but also intensifies safety training planning according to different scenarios such as "suspicious bags and explosions," "poisonous chemicals" or "train or station random homicide"; when actual manmade disasters occur, different execution plans are drafted according to crisis prevention, actual response, clean-up and restoration, etc. The relevant instructions are as follow:
- Crisis prevention stage:THSRC police are engaged to assist in maintaining station order and safety of train services, and a security company is also contracted to maintain order at stations, right-of-way of equipment, and safety of train services. In addition, dedicated personnel are assigned to monitor the closed-circuit television cameras at various stations, important server rooms along the rail, or tunnel entrances. For detailed information on security management, please refer to the "Partner Relationship Management and Local Supply" chapter of this report.
- Actual response stage:In the case of man-made safety incidents, THSRC will immediately activate the crisis management and control mode. The key actions include rescue, evacuation guidance, isolation of the scene, access control, and notification of railway police.
- Clean-up and recovery stage:After the on-site investigation and evidence search are completed and approved by the judicial authority, the on-site clean- up and recovery operations will be carried out. In the early stage of resumption of operations, inspections and patrols will be enhanced, and the scale of the police on duty will be increased as support.
Regarding the handling of abnormal equipment, THSRC carries out the repair and maintenance of circuit boards/modules of all train cars of the train system, the repair and maintenance of the switch of the signal system and electronic equipment, and turnout equipment reliability improvement project through the electronic maintenance center, while auditing and inspecting the maintenance records to strictly control the safety of the transportation equipment. In order to maintain the reliability of important system equipment, a mid- to long-term maintenance plan has been established to extend the life of the equipment, as listed below:
- Complete the renovation project for the Disaster Warning System (DWS) slope detector
- Initiate signal automatic train control (ATC), electronic Interlocking System (EI) unit midterm maintenance
- Establish an intelligent real-time analysis and fault prediction system for dissolved gas
- Install a CCTV system to record the front-facing view of the train
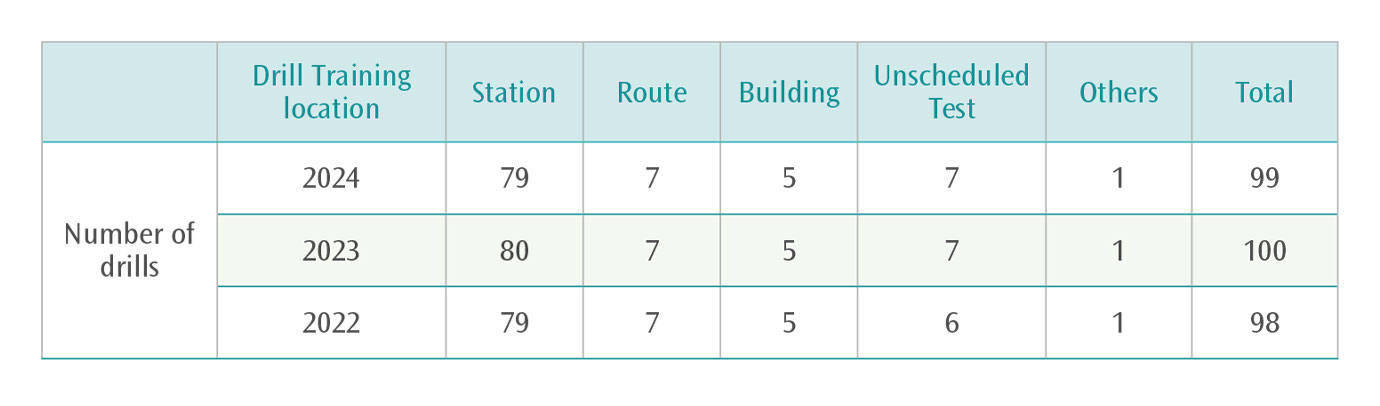
In addition to planning overall preventative and contingency measures based on three types of hazard factors such as natural factors, human factors and equipment abnormalities, the THSRC has also conduct regular and unscheduled drills for various hypothetical scenarios, so that employees at all levels are familiar with the emergency response procedures for various kinds of emergencies. In 2024, to part with the haze of the epidemic, we expanded safety training and disaster prevention and rescue exercises to improve the emergency response capabilities of various units. We continue to refer to the experience of various railway incidents at home and abroad and the “Taiwan High Speed Rail Overall Disaster Prevention and Response Plan” approved by the Disaster Management Council of the Executive Yuan, the laws and regulations, the requirements of government units and the review of abnormal incidents of highspeed railway companies, to formulate an annual disaster prevention and rescue exercise training plan, and plan and promote various disaster prevention training and rescue exercises with foreign aid units in various places to familiarize ourselves with the joint command and response mechanism, and improve onsite rescue and prevention capabilities. In 2024, THSRC conducted a total of 99 disaster prevention and rescue drills (training) at various stations, depots, and routes, which 100% completed as per scheduled.
Safety Training Categories in 2024

Note: Outsourcing units include the Chemicals Administration, Ministry of Environment, fire protection, police, health department, environmental protection, and medical response center, as well as environmental incidents specialist teams.
Disaster Prevention and Rescue Drills Training Record
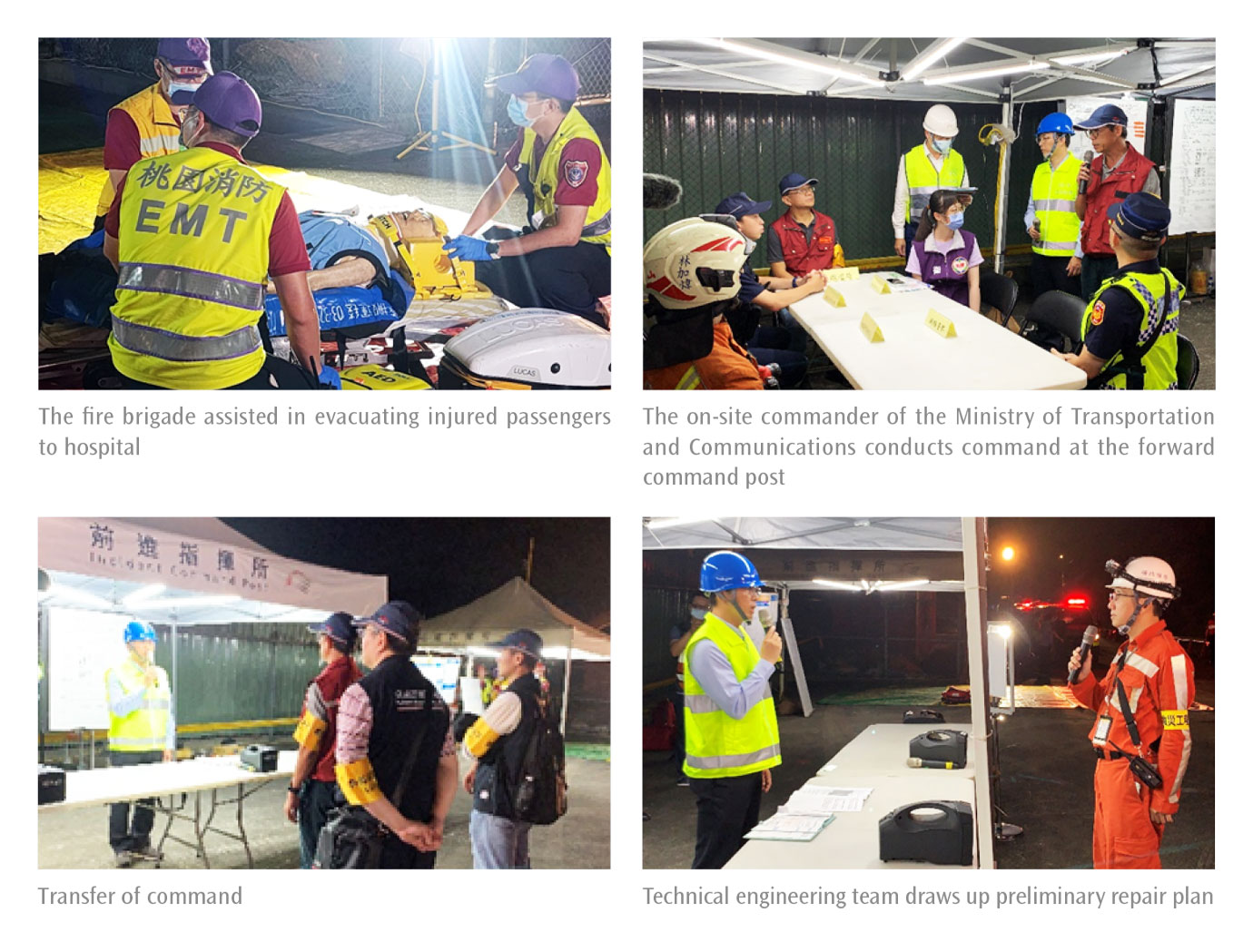
Large-scale Joint Drills and Training Events in 2024
THSRC conducts various disaster prevention drill exercise annually to simulate the response measures after disasters occur, so as to reduce the impact of accidents and improve the overall disaster prevention and response capabilities. After more than three months of discussion and preparation, the "On-Track Passenger Evacuation Drill Due to Slope Failures at the North Exit of Linkou Tunnel" was conducted on the night of May 30, 2024. The drill simulated extreme weather conditions caused by global warming and several days of heavy rainfall. As a high-speed rail train entered the Linkou Tunnel, it encountered a landslide at the tunnel's north exit. The Disaster Warning System(DWS)rockfall detector was triggered, prompting the train to receive an emergency stop signal and activate the Urgent Brake(UB)system. As the train passed the north exit of the Linkou Tunnel, it was struck by the landslide, resulting in damage to the rear carriage and injuries to some passengers. The landslide also disrupted the overhead power lines outside the tunnel, causing a power outage. The authorized train crew promptly guided passengers to evacuate through the emergency escape exit. External emergency response units and the station disaster response team arrived shortly after to assist with the evacuation. In addition to mobilizing relevant company personnel and security contractors, approximately 200 participants took part in the drill. These included teams from the Taoyuan Fire Department, Police Department, Health Bureau, Railway Police Department, and the Railway Bureau, all working together under a coordinated response effort.
On-Track Passenger Evacuation Drill Due to Slope Failures at the North Exit of Linkou Tunnel

In order to implement consolation and immediate medical care for injured passengers and their families when major disasters happen, THSRC has established the “Care and Consolation Team” in North, Central, and South part of Taiwan to provide relevant support and company, including care and consolation telephone lines, family contact, medical assistance, legal consultation, and funeral and other consultation on various needs. Team members also regularly participate in the annual disaster prevention and relief drills (training), reviewing and optimizing their mobilization effectiveness through actual drills.
The command of the overall operation system of THSRC is controlled by the Taoyuan Operation Control Center(OCC), including route control, signaling and safety interlock, power control, communication, data transmission or monitoring alarms equipment. Through 24 / 7 real-time monitoring, THSRC keeps abreast of the status of the operation and night maintenance along the entire HSR line while maintaining close contact with the station control centers, depot control centers, and external emergency supporting units to ensure transportation safety.
