Safety Transportation

Safety Services and Responsible Transportation
Safety is the operating principle and core value of THSRC, and is also the responsibility and commitment to every passenger. We monitor operational safety through a sound management structure and continue to consolidate the culture of safety first. During the 17 years of operation, we have always maintained zero operation accident. In 2024, the THSRC has an average daily ridership of nearly 214,000 passengers, approximately 14,000 more passengers than last year, an average delay time of only about 0.20 minutes and a train punctuality rate has reached 99.50%. This is a clear demonstration that THSRC provides high-speed rail travel services that can be trusted by the public.
-
Dedicated Safety Management Framework
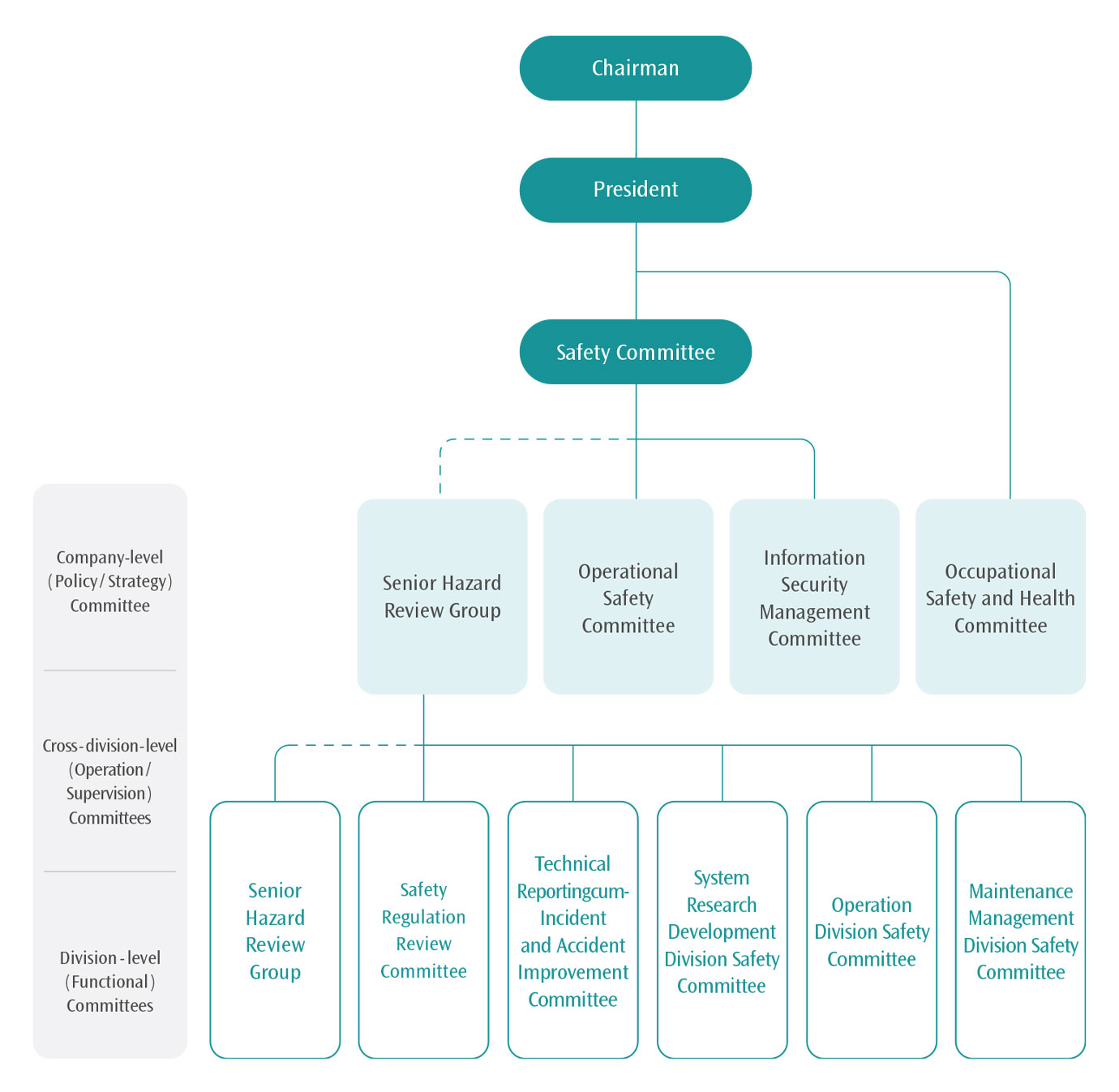
In order to ensure the safety of THSRC's operating environment, the Company has set up safety committees at 3 different levels to formulate prudent safety policies and implementation plans by the company-level safety committee, and regularly report significant issues related to operational safety to the Board of Directors. The cross-division-level Operational Safety Committee, functional committees, and division-level committees, executes strategies to ensure that each employee understands and abides by the Company's safety regulations. In addition, the employee work instructions stipulate that employees shall be assigned the management or execution responsibilities as per their job rankings to thoroughly implement safety management measures and shape a safety-oriented operating culture.
-
Organizational Chart of Safety Committee
Descriptions of Safety Committees at All Levels
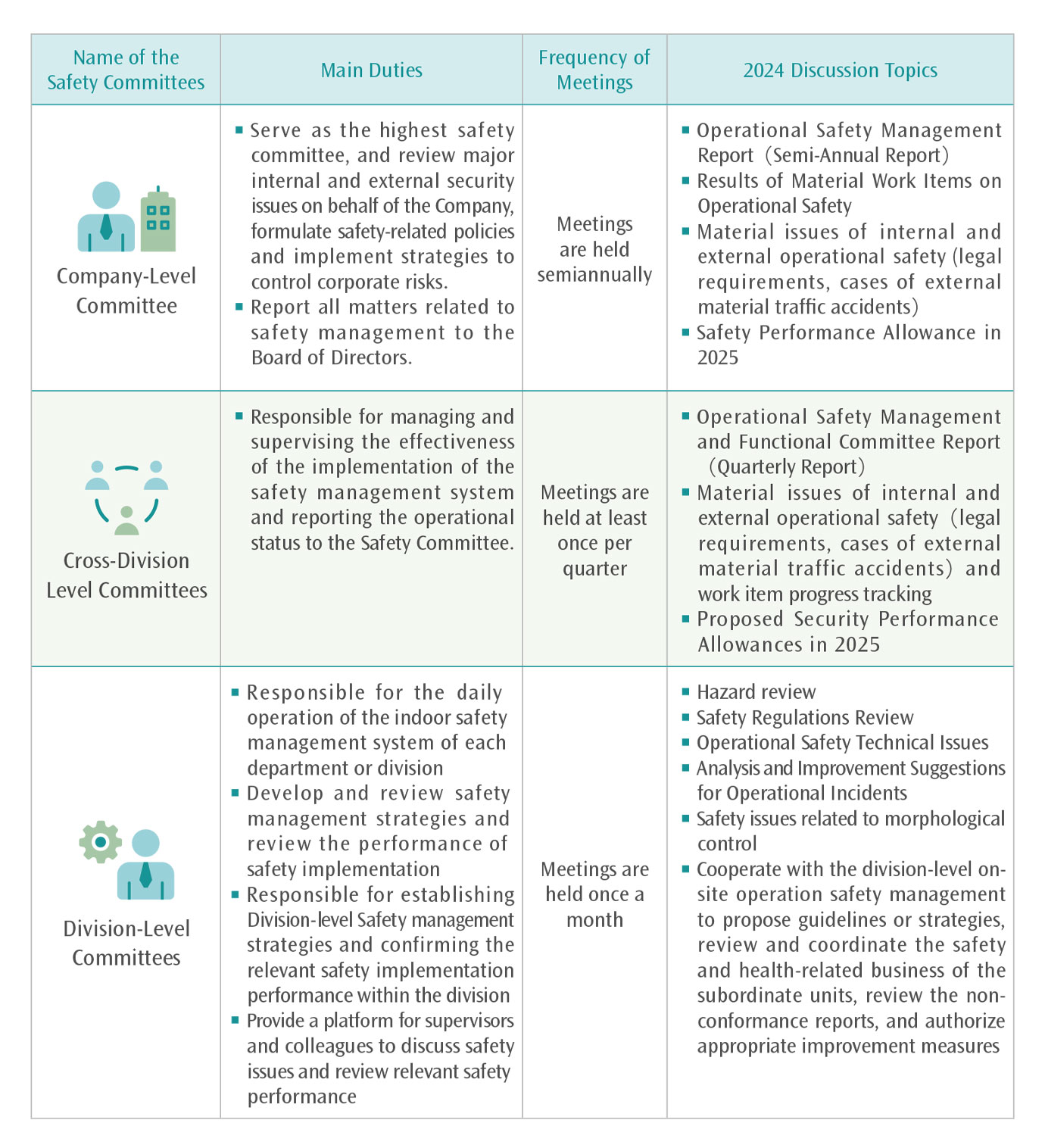
Note: The Company-level Safety Committee convenes a meeting every six months. The Occupational Safety and Health Committee, as well as the Operational Safety Committee and the Information Safety Management Committee at cross-division-level convene a meeting every quarter. The Operation Division Committee, the Maintenance Management Division Safety Committee, the System R&D Safety Committee, and the Hazard Review Group(HRG) at division-level convene a meeting every month. The "Operational Safety Committee" and the "Technical Reporting-cum-Incident and Accident Improvement Committee" decide whether to convene meetings depending on the occurrence of the incident, with no fixed frequency of such meetings.
-
Operational Security Mechanism and Safety Management System
THSRC has implemented an operational safety management mechanism in order to mitigate and control safety hazards. It effectively applies internationally recognized risk assessment and safety management methods, ensuring that every operational process is executed according to the procedures. Quarterly, THSRC conducts comprehensive reviews on significant railway operational safety issues from the perspectives of legal regulations, systematic transportation, extreme disasters, safety management, and security affairs, both domestically and internationally. These findings are then presented to the Operational Safety Committee for review.
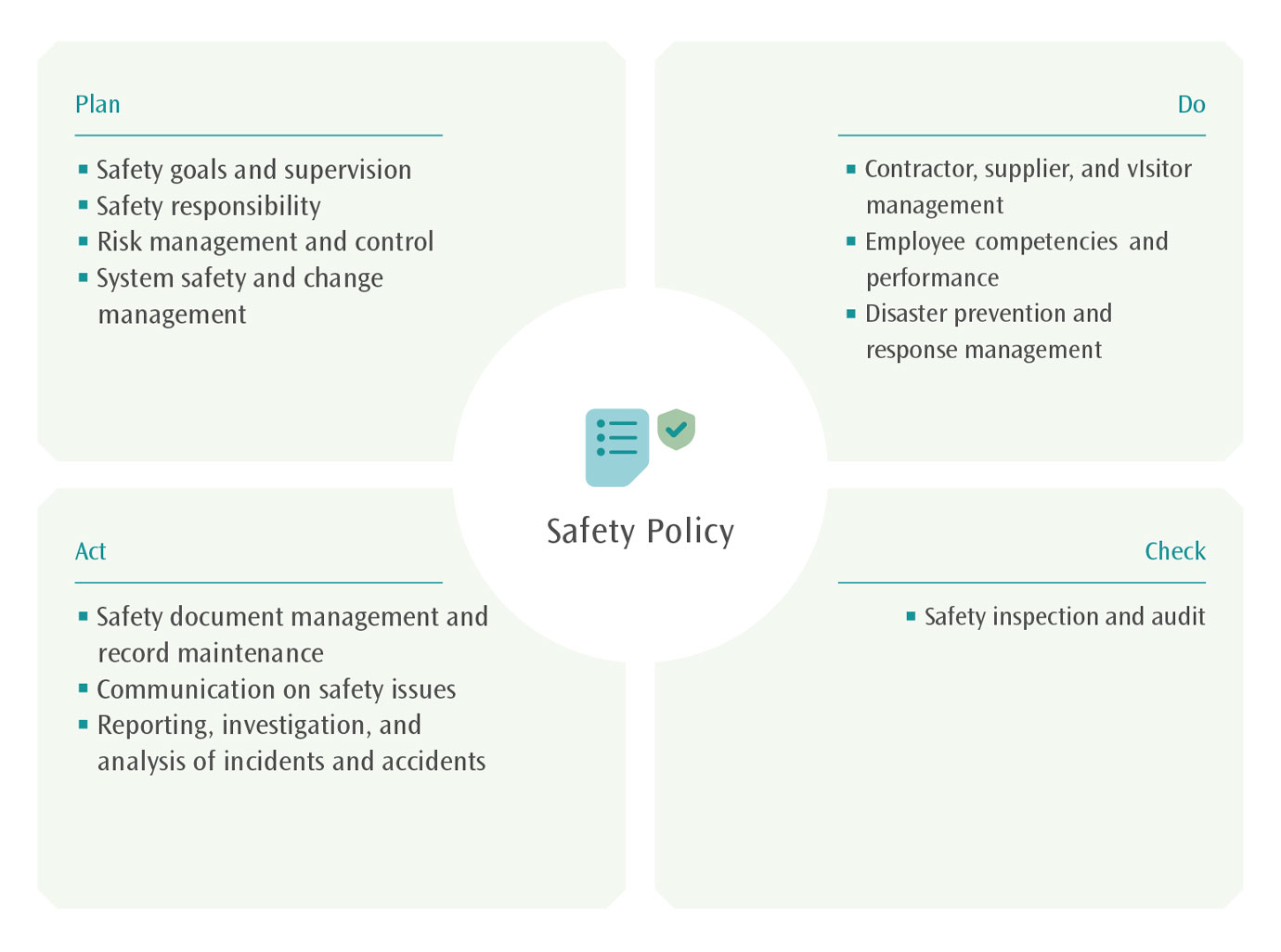
The THSRC has established a safety management system (SMS) for many years, formulating the "Operation Safety Plan" as the highest level of safety management guidelines. The plan encompasses 12 safety management elements, and through the P-D-C-A (Plan-Do-Check-Act) principle, continue to control, supervise, improve the safety performance of the railway transportation system. This approach effectively achieves the goal of prioritizing safety. In response to the amendments to the Railway Train-Control Rules in 2022, which require railway organizations to implement safety management systems, THSRC also cooperates with the regulator to promote safety management mechanisms. The Company has drawn on the experiences of international transportation and standardization organizations (such as the European Union Agency for Railways, the International Civil Aviation Organization, and the International Organization for Standardization) and references the results of previous safety management system reviews conducted by THSR (including incident/accident investigations, operational safety audits, and major internal and external issues). Based on these inputs, significant modifications have been made to the Operational Safety Plan, taking effect on January 1st, 2023.
-
-
Safety Culture Promotion and Communication
In order to strengthen the safety awareness and culture of THSRC colleagues and partners on the protection of THSRC as a key infrastructure, we held 3 "Railway Industry Security Work Symposiums" in 2024, including "Identification of Hazardous Materials," "Security Response Training" and "Critical Infrastructure Seminars" to promote cross-functional communication among colleagues in various units and jointly shape safety awareness. A total of 104 trainees participated, including front-line maintenance executives and supervisors. We look forward to effectively improving THSRC overall protection preparedness and emergency response capabilities through expert sharing and cross-unit discussions, and continuously improving the quality of security in the face of various types of threats and challenges.
-

The THSRC places great emphasis on operational safety and actively promotes a wide range of safety measures while maintaining ongoing communication with external stakeholders. In 2024, the company hosted two major media events, including the groundbreaking ceremony for the "Second Vehicle Maintenance Plant," where the company showcased the expansion of maintenance capabilities to ensure operational safety. Following the April 3 Hualien earthquake, THSRC demonstrated the professionalism and responsiveness of its Operation Control Center by fully restoring services across the entire line within five hours. Through these media engagements, THSRC aims to communicate its high-standard operational safety mechanisms to the public and to reinforce its corporate philosophy of "Safety First" in the minds of passengers.

-
Safety and Quality Service
THSRC regularly reviews the effectiveness of quality management through a rigorous quality management system, various quantitative quality performance indicators, and quality improvement proposals, and promotes quality policies from top to bottom, so that the spirit of quality becomes the High-speed rail culture, to protect each passenger who trusts THSRC.
-
Quality Management System (QMS)
The Company introduced the ISO 9001 quality management system since 2005, and annual quality management review meetings are held since 2007, chaired by the General Manager and attended by various company's various supervisors. Since 2010, THSRC has been verified by external third-party annually in accordance with the ISO 9001 international standard. The certification covering the overall core business in "high-speed rail operation, maintenance and passenger service" has been successfully passed. Regarding the regular and irregular inspections conducted by the Railway Bureau of the Ministry of Transportation and Communications, the relevant observations and suggestions issued in 2024 did not immediately affect the operation, and all have been improved and removed from the list. Thus, there are no issues that need to be improved in 2024.
-
External Quality Inspection Items
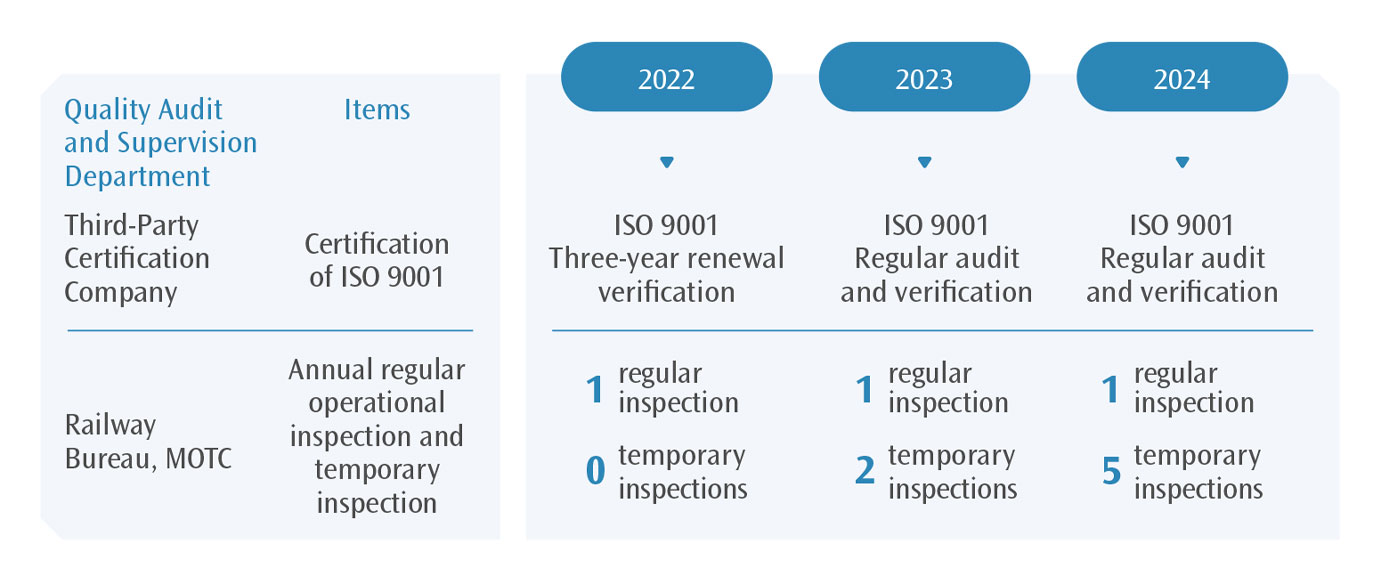
In order to thoroughly implement quality management, the THSRC regularly checks the latest status of internal operating facilities, equipment and related systems, software and hardware, and ensures that the THSR's quality management system keeps pace with the times through strict control and inspection of internal operating quality, and continuously strengthens the operation and maintenance quality.
Examination of Internal Configuration
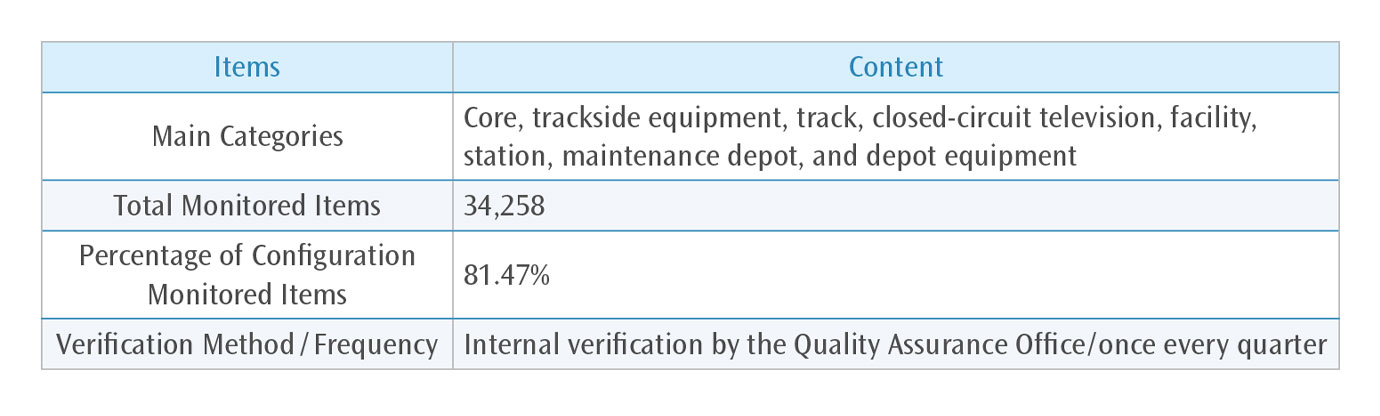
-
Quality Management Performance Review
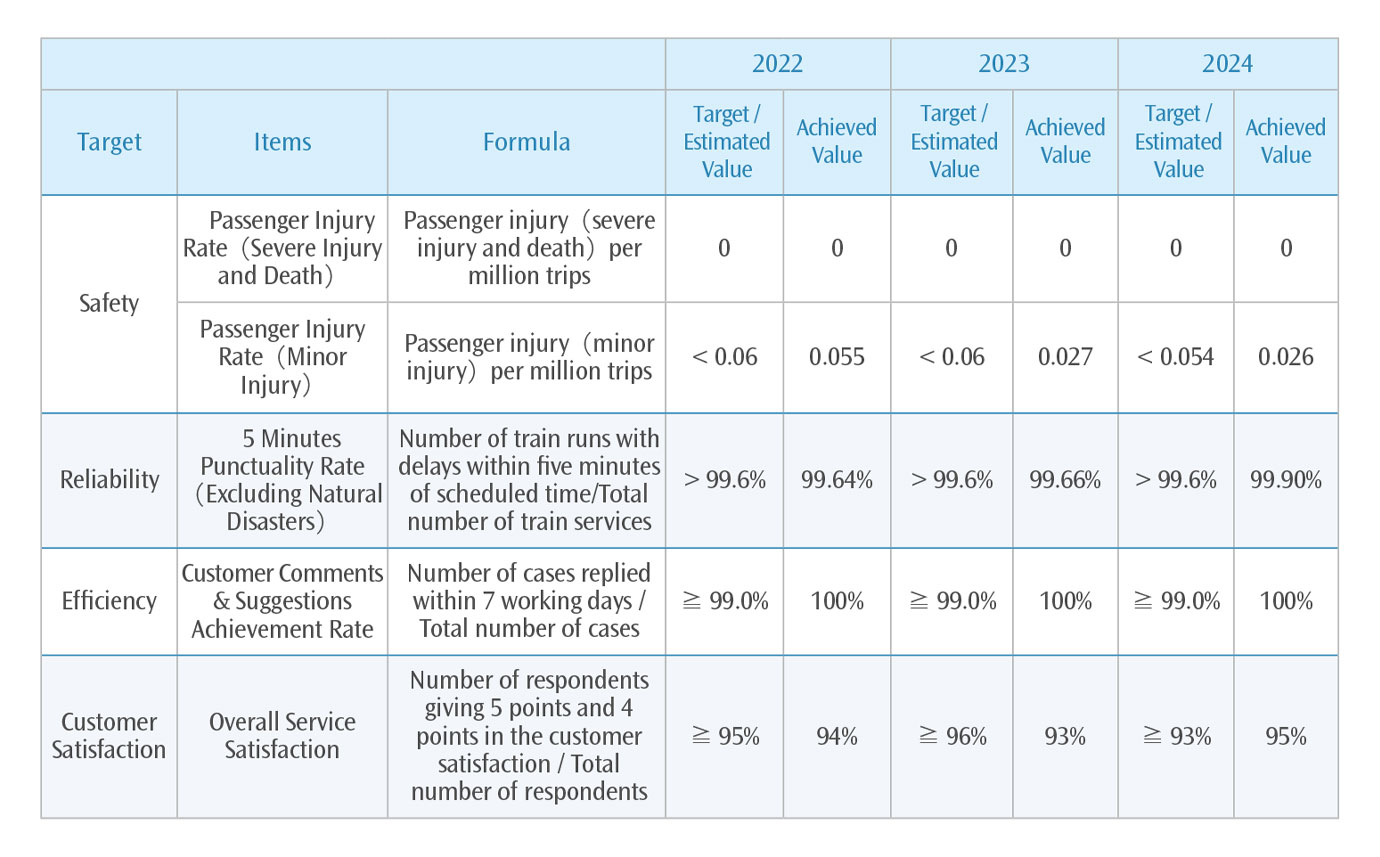
THSRC has established various internal performance indicators for quantification of quality and reviewed and improved those tasks by following up on the results quarterly, so as to provide customers with high quality travel services in line with four major aspects of "safety," "reliability," "efficiency" and "customer satisfaction." The number of serious injuries and deaths caused by traffic accidents on the THSRC in 2024 is 0; while the number of minor injuries to passengers is 2, which is the same as in 2023. The passenger injury rate(minor injuries)of the "safety" performance indicator for the current year is 0.026 per million trips, which meets the set goals/estimates, which demonstrates that we focus on continuing to improve quality management and provide passengers with safe and high-quality travel services.
-
Quality Performance Indicators
Since 2011, THSRC had launched an employee suggestion improvement system and introduced quality control circle(QCC)activities every year, encouraging employees to apply innovative thinking and technology as the foundation for developing practical proposals to optimize quality control and operational performance, continuously resolve various issues, and effectively reduce operation and maintenance costs. Since the implementation of the proposed improvement system in 2011, the total savings had reached NT$96 million.
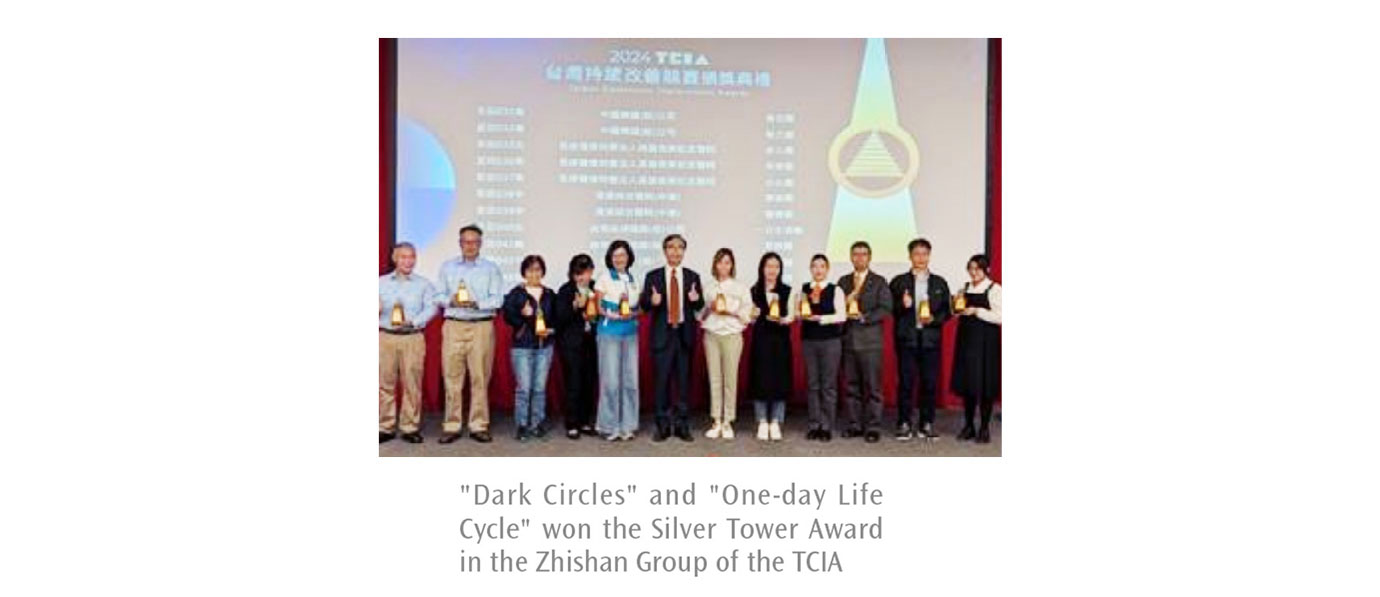
Since 2009, the QCC program had been promoted, which resulted in cumulative savings of over NT$300 million. In 2024, the annual cost savings amounted to NT$10,917,000, with a cumulative manpower saving of 55,000 man-hours, and 7,597 man-hours saved in 2024 alone – significantly improving production efficiency, promoting collective investment, enhancing the quality, safety, and efficiency of high-speed rail services, and further elevating the overall passenger experience. This also reinforced the positive image of THSRC as a company that prioritizes safety and quality. In 2024, the QCC teams of "Dark Circles" and "One-Day Life Circle" were both awarded the highest-level Zhishan Group Silver Tower Award from the Taiwan Continuous Improvement Awards(TCIA), representing strong public recognition of THSRC's efforts in quality improvement.

-
Station and Route Safety and Risk Management
Maintaining the smooth operation of tracks is the core of safety management of THSRC. THSRC's track maintenance personnel perform routine inspections after daily train operations. In addition to routine track inspections, daily maintenance and examination of THSR facilities includes stations, trains, mechanical and electrical facilities, civil structures, and route safety, which covers the safety inspection of various facilities. At the same time, various professional technologies are used to maintain transportation safety, such as Train Vibration Automatic Measurement, Ultrasonic rail inspection, Rail and turnout grinding and other daily maintenance operations. The actual safety inspection performance in 2024 includes a total of 1,800 turnout inspections, and routine track inspections and track irregularity inspections of 8,421 kilometers.
-
Train Inspection and Maintenance Performance in 2024
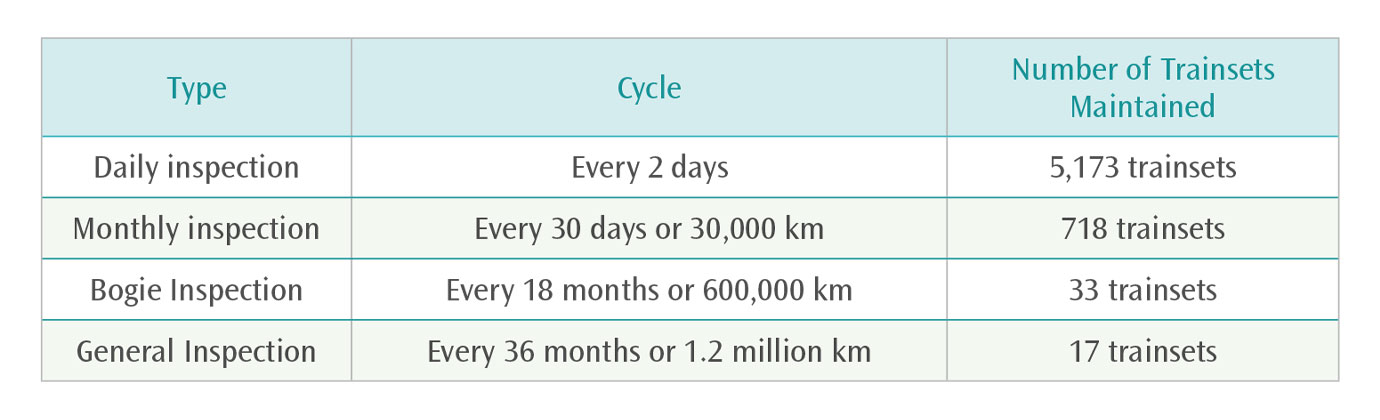
Other Railway Maintenance Management Plans

THSRC has established a Hazard Review Group to implement risk management and control. The group is comprised of professionals from various fields within the company. It holds a monthly regular meeting to review hazard information and identify hazard risks while confirming whether appropriate procedures and technologies are implemented so as to put forth countermeasures to mitigate such risks.
As for the end of 2024, all hazard risk levels identified at the HRG meetings were within the acceptable risk tolerance range. THSRC's regular or irregular inspections will continue to be carried out by local engineers and security personnel, and the "hazard control record sheet" will be updated monthly to reduce the risk of such hazards. In 2024, there was one railway safety incident involving a leakage and ignition of lubricating oil due to a fractured hydraulic pipe on engineering vehicle MFV2001. The primary cause of the fire was the rupture of a test hydraulic gauge installed on the vehicle's gearbox - a component not originally designed to be part of the system. The leaking oil of the gearbox spread to the high-temperature components of the turbocharger cylinder, ultimately igniting. No injuries were at the scene, and the operation of trains was not affected. In response, THSRC reviewed fire hazard identification and mitigation measures for relevant engineering vehicles. Testing procedures were proposed for temporary equipment installations or hardware/ software modifications made to meet external testing requirements. These procedures include change documentation, examination methods, corresponding safety measures during the test period by both users and maintenance units, equipment removal after testing, and follow-up actions. These measures aim to reduce risks associated with control project modifications and prevent similar incidents in the future.
