Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation

Climate Change Mitigation Strategy
In light of the increasing global concern regarding climate change, the government's commitment to achieving net zero emissions by 2050, and the rail transportation industry's response to the threat of climate change, THSRC acknowledges the potential impact and difficulties that climate change may pose to sustainable operations. As a result, THSRC has proactively implemented a range of measures to mitigate and adapt to climate change.
In 2024, THSRC implemented a mechanism to evaluate climate-related risks and opportunities based on the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) framework's four major recommendations and eleven recommended Disclosure. The objective is to assess the impact of climate change on the Company, implement systematic adaptation measures to mitigate the Company's effects, and improve operational resilience. The TCFD requirements encompass the following four recommendations:
Governance
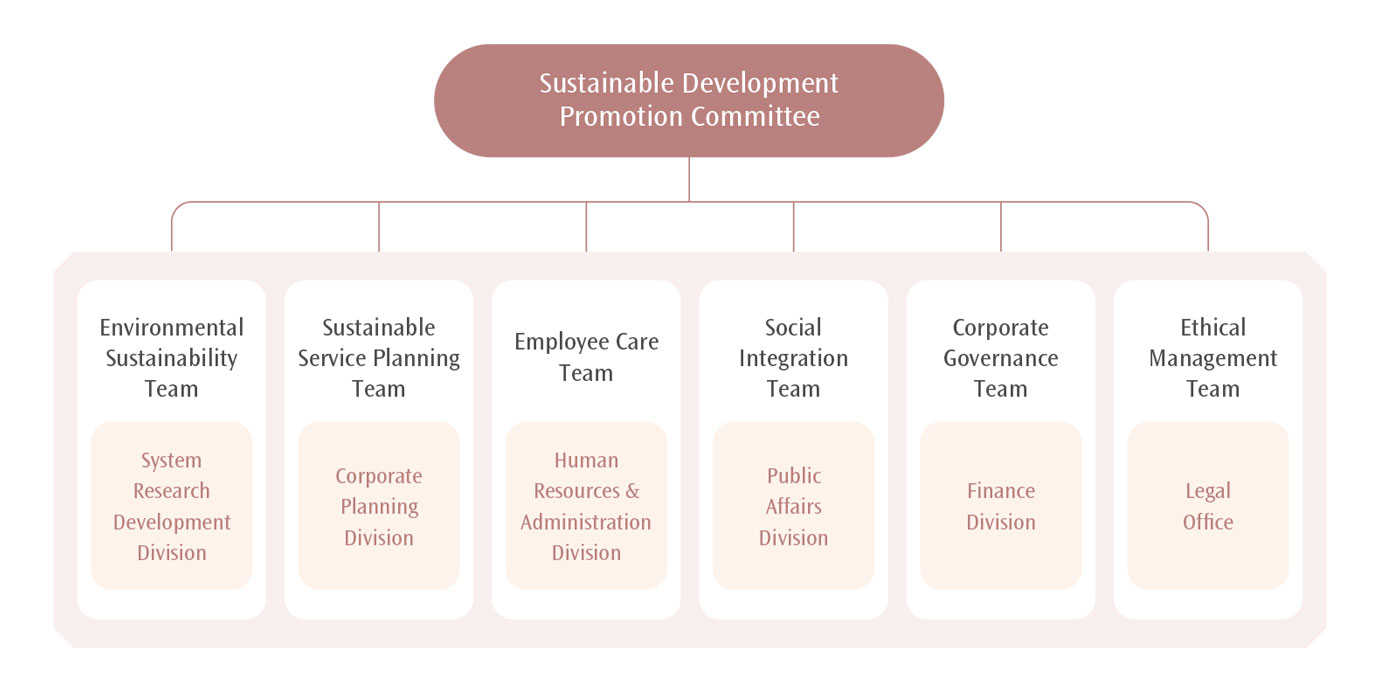
THSRC has established the “Sustainable Development Promotion Committee” under the “Sustainable Development & Nominating Committee” of the Board. The Sustainable Development Promotion Committee is overseen by the Board and the Chairman, and is composed of the President and senior executives from managerial departments. The Sustainable Development Promotion Committee's six sustainability teams continue to focus on internal corporate issues related to sustainable management, and reports implementations and achievements to the Sustainable Development & Nominating Committee and the Board every year. Climate-related governance, strategies, responses, and promotions are coordinated by the Environmental Sustainability Team through jointly formulated strategies, targets, and action plans associated with climate change, nature, and net zero issues.
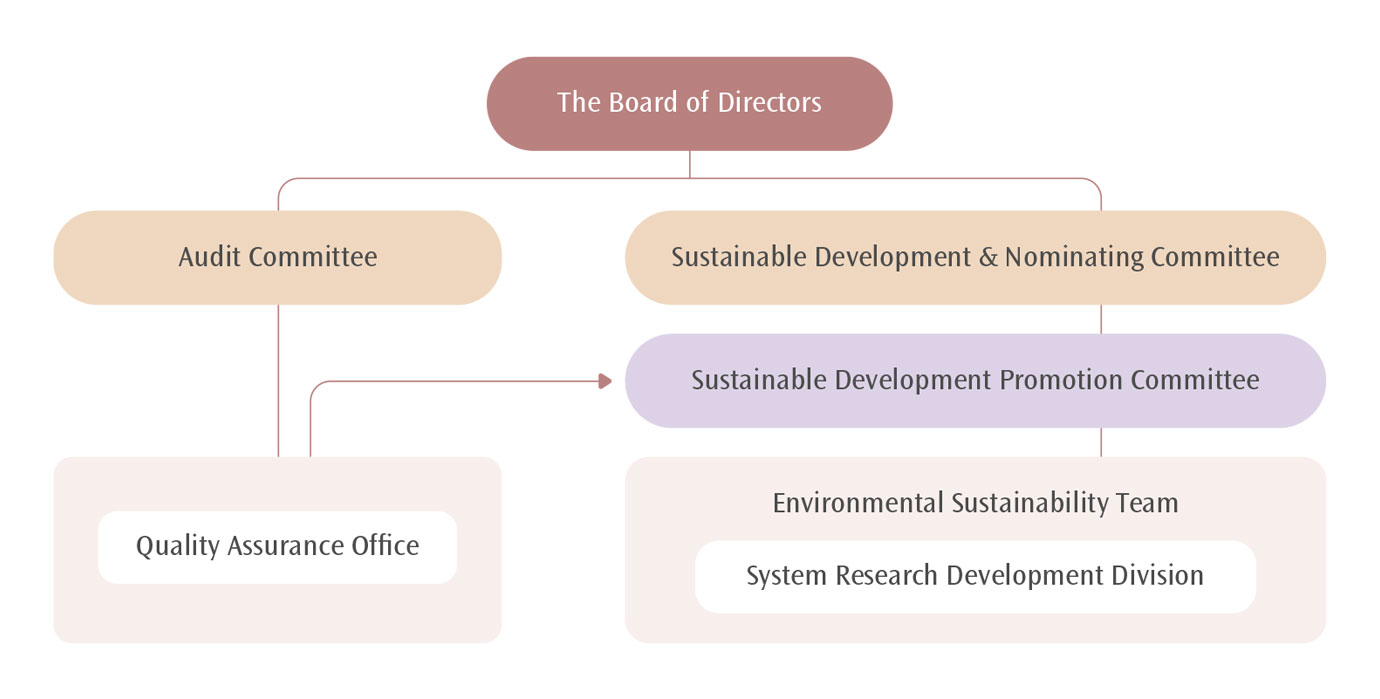
The Company has formulated “Risk Management Policies,” and the Audit Committee under the Board which is responsible for supervising and establishing overall risk management mechanisms, including risk management structures that encompass all Corporation operations. The Environmental Management Committee established under the Audit Committee is responsible for supervising, implementing, and regularly reviewing environmental risks and targets, as well as communicating environmental management matters. The Committee is chaired by the President and is composed of top executives from various departments, facilitating interdepartmental communications that are beneficial for overall operations. A number of interdepartmental working teams have been established under the Environmental Management Committee to implement environmental management tasks. Additionally, risk management structures, risk management promotions, and implementation units are reported to the Board once every year to facilitate monitoring of related climate risks, and to review actions and achievements associated with climate change responses.
In addition, to align with IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standard S2 “Climate-related Disclosures,” the risk management framework has incorporated climate risks, forming a dual-track management mechanism. The overall risk management is supervised by the Quality Assurance Office under the Audit Committee.At the same time, climate risk-related strategies, metrics, and targets are planned and executed by the Environmental Sustainability Team under the Sustainable Development Promotion Committee, with regular reporting to the Board of Directors and the Sustainable Development & Nominating Committee. The organizational structure and operational mechanism are as follows:
| Responsible Department | Roles and Responsibilities | Implementation Status |
|---|---|---|
| Quality Assurance Office | Risk Management |
|
| Environmental Sustainability Team | Climate Risk Strategies, Metrics and Targets |
|
Strategy
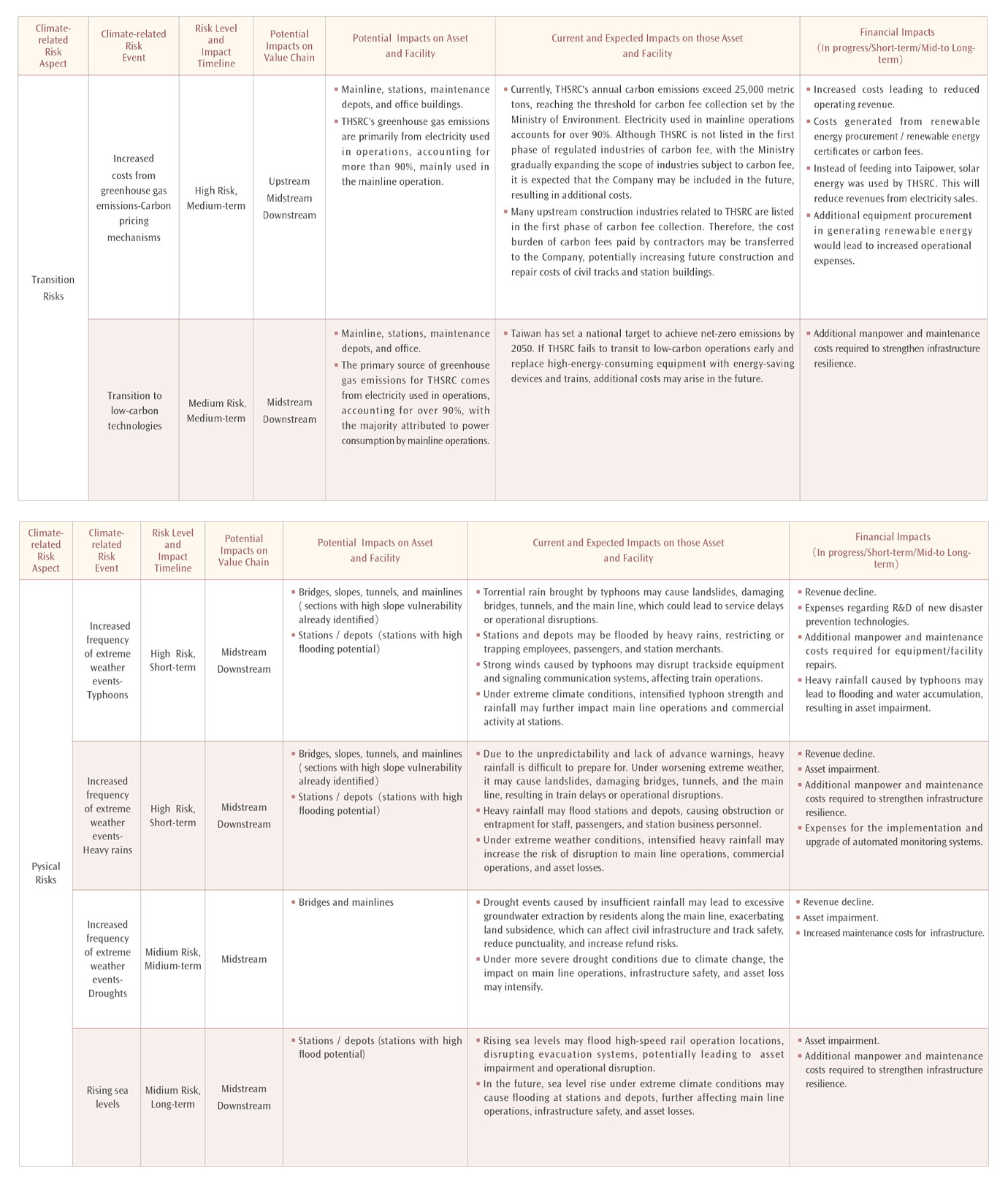
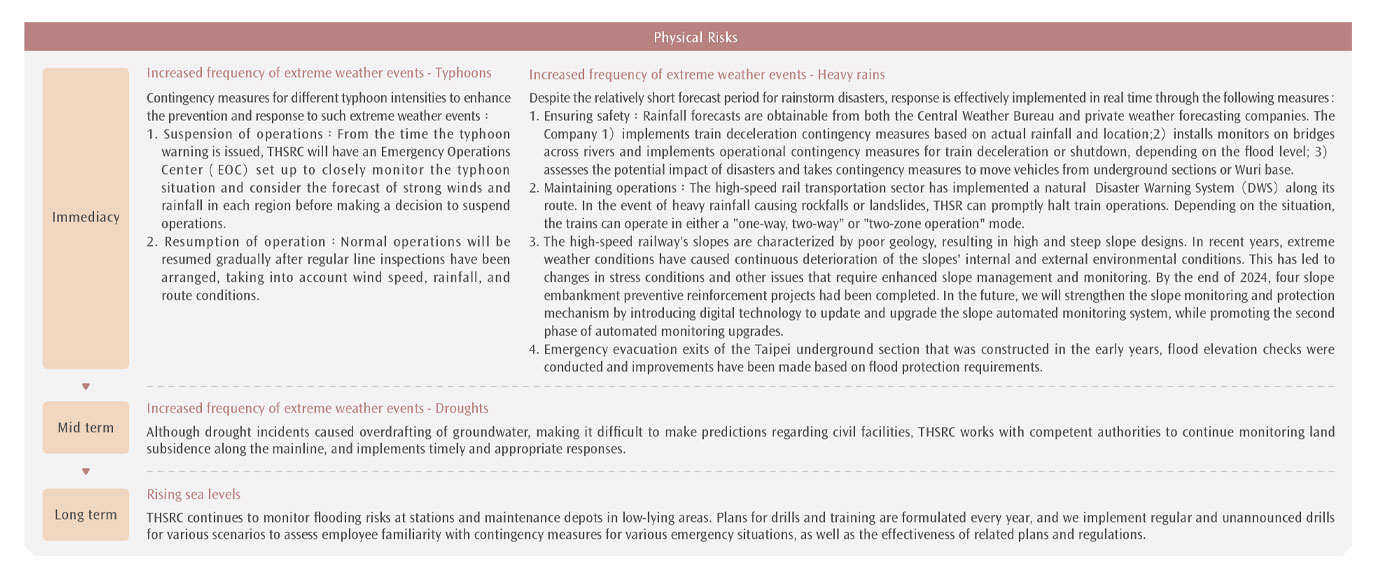
THSRC conducted a comprehensive assessment of climate change risks and opportunities referring to the TCFD disclosure framework. At the same time, the Company continues to introduce scenario analysis and financial quantification of risks, and the results will be disclosed in subsequent reports. The latest climate risk assessment was completed by the Company at the end of the 2024. Taking into account the unique characteristics of the railway transport industry and prioritizing internal natural disaster management practices, the assessment identified 3 moderate risks and 3 high risks from 12 climate-related risks, including 2 transition risks and 4 physical risks. A timeline of potential impacts of climate risks is also incorporated into the transformation plan. The periods of impact are classified as short-term (2024–2026), medium-term (2027–2035), and long-term (2035–2050). The response actions and related financial descriptions for managing climate risks will be disclosed in subsequent reports. Please refer to the table below for the results of this evaluation.
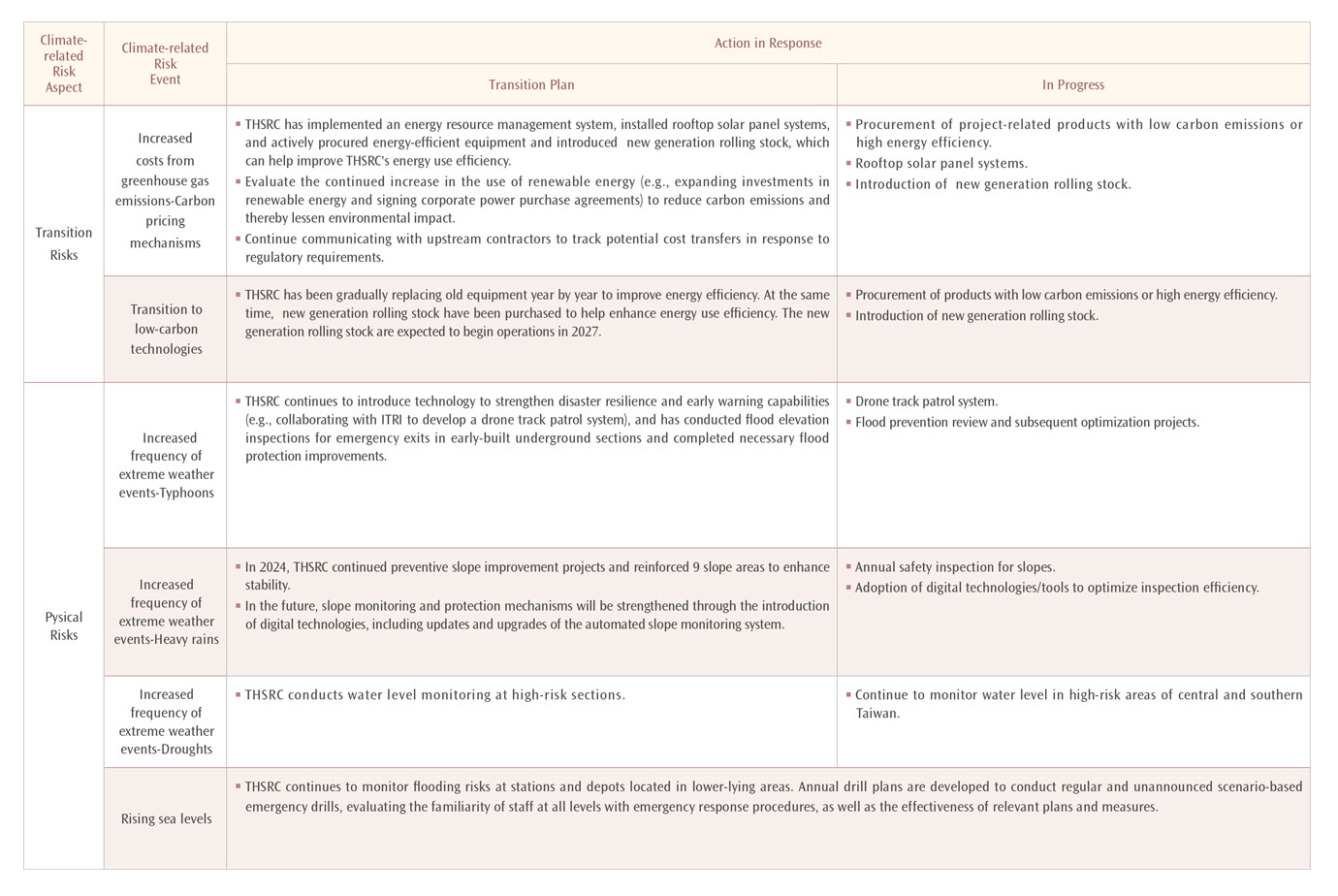
Based on the results of the climate risk assessment mentioned before, THSRC has established the guidelines for adverse weather operations, and implemented corresponding actions based on physical risks. Currently, the Company has already developed a sound early warning mechanism for climate-related disasters and will further enhance the disaster tolerance of track-related infrastructure and the climate resilience of operating system. This will ensure the provision of safe and secure services, allowing passengers to travel safely.
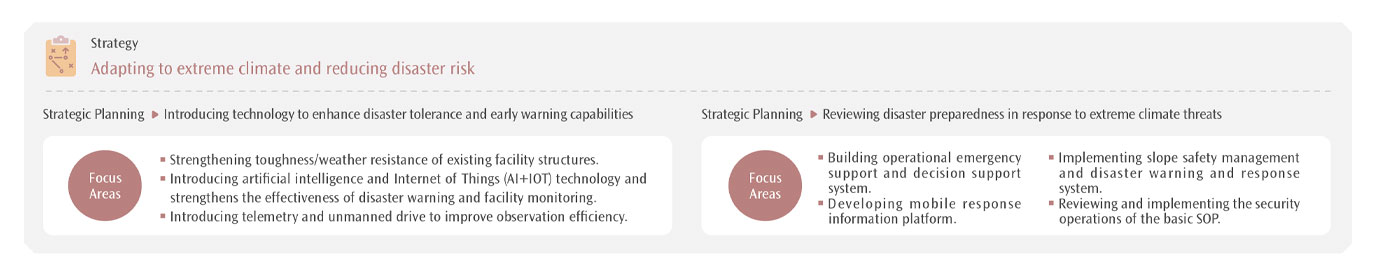
One of the six primary axes of THSRC's sustainability strategy, THSRC's medium to long-term strategic blueprint for the next five years, is to address the impact of extreme climate and mitigate disaster risks. To achieve this, THSRC will actively collaborate with government agencies, academic institutions, and relevant industries to enhance climate adaptability, minimize operational disruptions, and reduce financial losses.
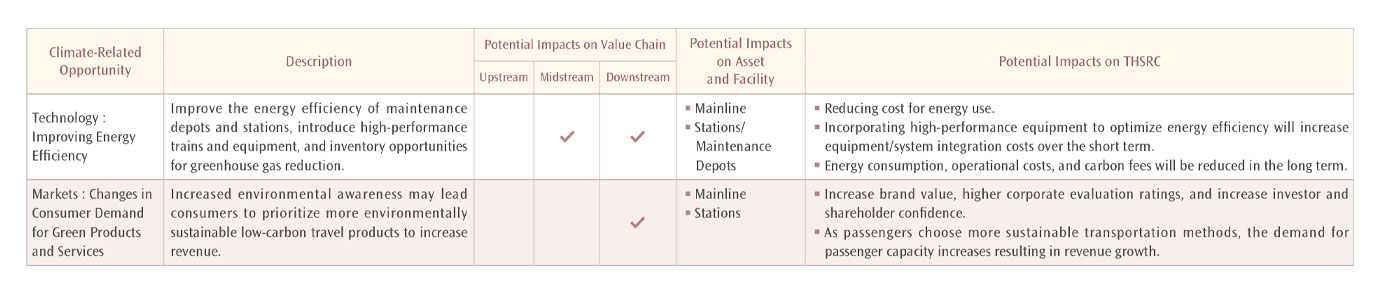
Climate change presents both risks and opportunities for businesses. THSRC is capitalizing on the advantages of low-carbon transportation and plans to enhance the Company's efficiency by investing in renewable energy installations at stations and maintenance depots. The Company's goal is to establish a zero-carbon transport value chain. In addition to addressing climate risks, THSRC aims to offer consumers environmentally friendly, fast, and convenient services, thereby promoting sustainability throughout Taiwan. The following table outlines the climate-related opportunities identified in this review:
Risk Management
Process for Identifying and Assessing Climate-Related Risks
THSRC has completed the identification of climate-related risks and opportunities by following the TCFD recommendation and utilizing international railway transport industry practices. This was achieved through cross-departmental interviews and discussions, as well as reviewing and incorporating existing internal natural disaster management and response mechanisms. Qualitative assessment was used to determine the impact of climate change on the Company's operations and financial performance. The results will serve as a foundation for future risk review and decision making, with the aim of enhancing THSRC's climate risk management measures and strengthening the Company's ability to respond to climate change.
Identify, Assess, and Manage Climate-Related Risk Process and Integration of Management Systems
THSRC has established “Risk Management Policies” and “Risk Management Procedures.” We inventoried and identified possible operational and profitability risks based on operational and business activities, mainly considering the seven aspects of strategy, operations, environment (including climate change risks), finances, information, legal compliance, and ethics. We also established an operational framework by reviewing the integrity of corporate risk management measures and effectiveness of risk controls as well as assessing risks from material domestic and overseas environmental, social, and governance issues.
All risks (including environmental risks) proposed by our committees are compiled each year along with effective control measures for environmental risks proposed by business units, and are reported to the Board and the Audit Committee. In the future, our risk management units will continue to respond to internal and external changes in environmental conditions, review and amend new risk management policies, strive to implement mid- to long-term strategic plans and targets, strengthen risk awareness at THSRC, and make strides towards a vision of sustainable management.
Indicators and Targets
THSRC has committed to echoing global and domestic carbon reduction and net-zero goals, with the aim of formulating performance reduction and quantitative targets for greenhouse gases, water resource management, and energy management. The achievement rate of each indicator is regularly monitored and reviewed, and internal management policies are adjusted on a rolling basis, based on the results of the annual review, to mitigate the impact of climate change through target management.
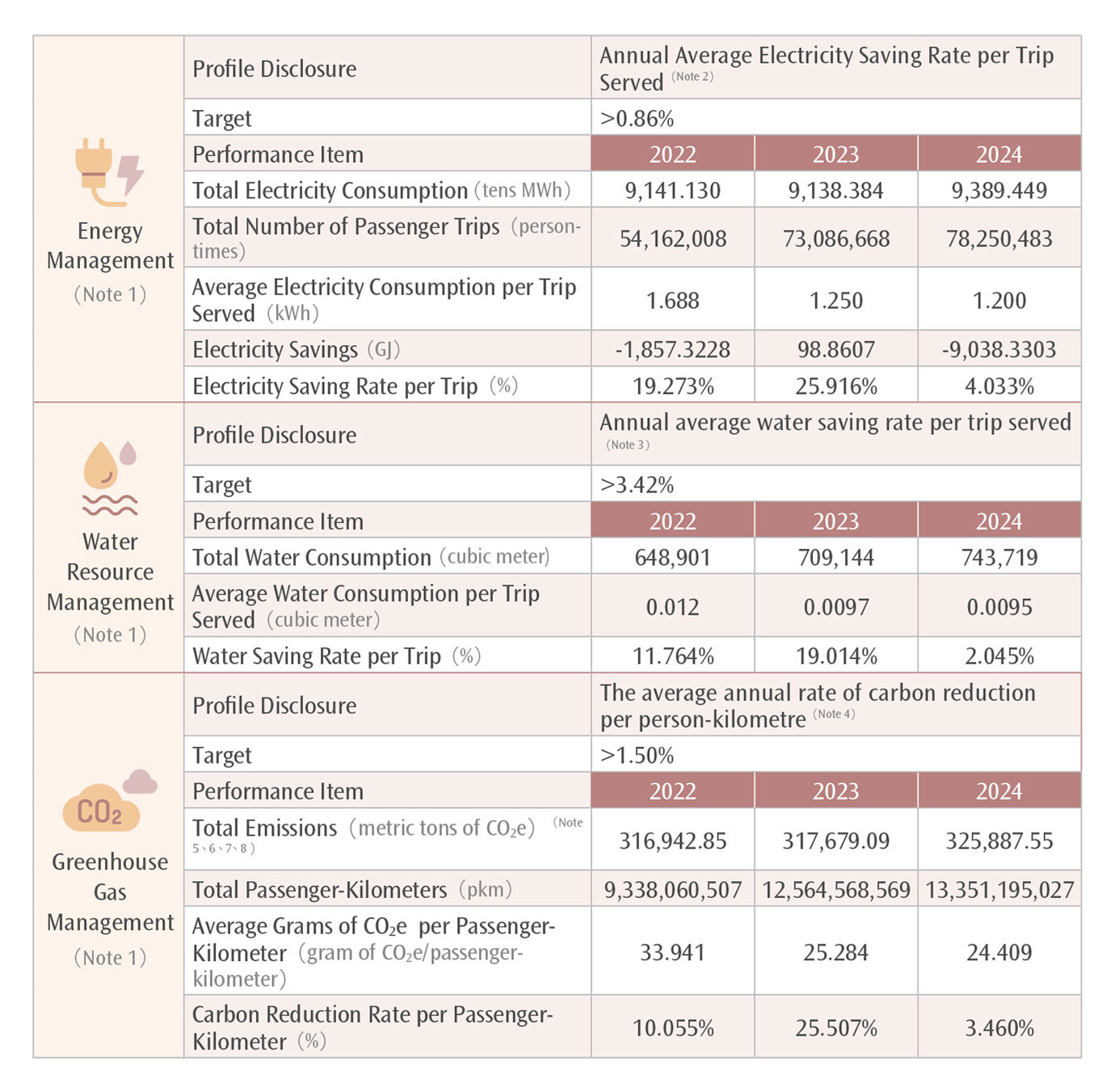
Notes:
1. Electricity, water, and carbon reduction rates were all calculated using corresponding intensity indicators, and we have established reduction targets based on the previous year to serve as a basis for internal energy management.
2. The scope of setting indicators and targets encompasses the electricity consumption of HSR stations, including the Taoyuan Operation OMC Building, but excluding commercial areas, parking lots, and public areas shared with the Taiwan Railways Administration (TRA) at Nangang, Taipei, and Banqiao stations, as well as depots.
3. The indicator and target setting scope pertains to water consumption at HSR stations, encompassing the Taoyuan OMC Building but excluding commercial areas, parking lots, and water consumption in public areas shared with TRA at Nangang, Taipei, and Banqiao stations, as well as maintenance depots.
4. The indicator and target setting scope encompasses the electricity and gasoline/diesel fuel consumption of THSR trains, as well as that of HSR stations. This includes the electricity consumption in public areas shared with TRA (at Nangang, Taipei, and Banqiao stations) and Taoyuan OMC Building, but excludes commercial areas and parking lots, depots, and THSRC's headquarters.
5. The emission factor of electricity is refered to the latest announcement from the Ministry of Economic Affairs.
6. The table are used for internal management and the figures were resulted from THSRC internal surveys of carbon emissions of electricity and gasoline usage covering the entire company, and do not include refrigerant, welding rods, CO2 fire extinguisher and Scope III emissions.
7. Emission factors for gasoline and diesel fuel in 2022、2023、2024 were corresponding from Version 6.0.4 (June 2019) of the Greenhouse Gas Emission Factor Management Table published by the Ministry of Environment.
8. GHG Emission = the amount of Electricity Consumption / Diesel procurement x the emission factor Global warming potential (GWP);Global Warming Potential (GWP) used in the Greenhouse Gas Inventory is from Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)'s sixth version assessment report in 2021.