Partner Relationship Management and Sustainable Supply Chain
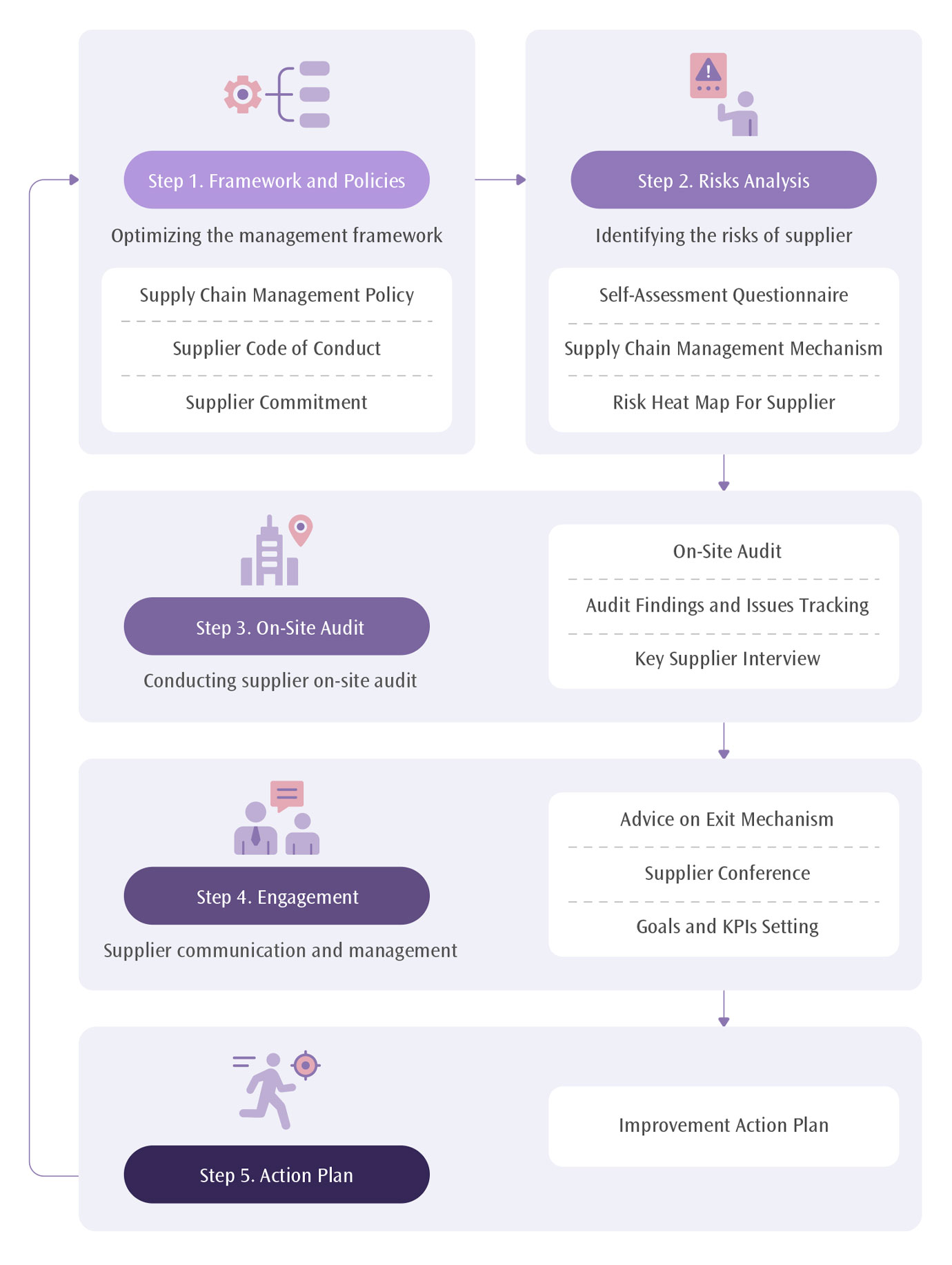
To enhance the overall supply chain sustainability performance, THSRC has formulated a supply chain management structure with reference to international standards and has continued the Company's implementation and optimization through a five-stage process. In 2023, THSRC launched a sustainable supply chain initiative to strengthen the Company's supplier sustainability management mechanisms, establishing a clear sustainable supply chain management policy. Through supplier risk identification, suppliers from various industries are classified and managed accordingly, with written and on-site audits conducted for medium-risk and high-risk suppliers. During the review process, THSRC actively communicates with suppliers and assists them in enhancing their practices related to environmental protection, occupational health and safety, and labor rights, ensuring that the suppliers not only comply with regulations but also advance toward shared sustainability goals with THSRC.
In 2023, THSRC optimized the "Supply Chain Management Policy" and "Supplier Code of Conduct," integrated the existing "Human Rights Policy" and expanded the scope of policy to all partners. These changes were announced to all suppliers in January 2024. We expect to strengthen domestic suppliers' sustainability through management mechanism. To align with global trends, we incorporated human rights and labor practice, safety and health, and environmental protection into the "Supply Chain Management Policy" and "Supplier Code of Conduct," especially improving suppliers' working conditions, gender equality, grievance mechanisms and labor practice issues.
In 2024, THSRC completed the revision of the supplier self-assessment questionnaire, aligning the topics with the contents of the Supplier Code of Conduct, aiming to collaboratively focus on key sustainability issues with supply chain partners. Over 100 completed questionnaires were collected. Based on the analysis of valid responses, suppliers were classified, and following documentary and on-site audits were conducted for those identified as high-risk. The 2024 on-site audits focused on ethics, human rights and labor, safety and health, and environmental protection. No supplier was found to have major deficiencies, nor was any supplier identified as posing significant potential negative social impact. Looking ahead, THSRC will continue engaging with key suppliers through communication, offering improvement suggestions, setting sustainability management goals, and formulating action plans. Through the five stages of its sustainable supply chain management framework, THSRC aims to gradually enhance the sustainability of Taiwan's rail supply industry and jointly build a sustainable supply chain with the Company's suppliers.
Sustainable Supply Chain Management