Material Topics
Identifying and Prioritizing Sustainability Topics
THSRC continues to pay attention to the international sustainability development trend and sustainability disclosure standards, and refers to the material issues of international benchmark enterprises. The THSRC Sustainability Report follows the GRI General Guidelines 2021 "GRI 3: Material Topics" issued by the Global Sustainability Standards Council to identify material sustainability topics.
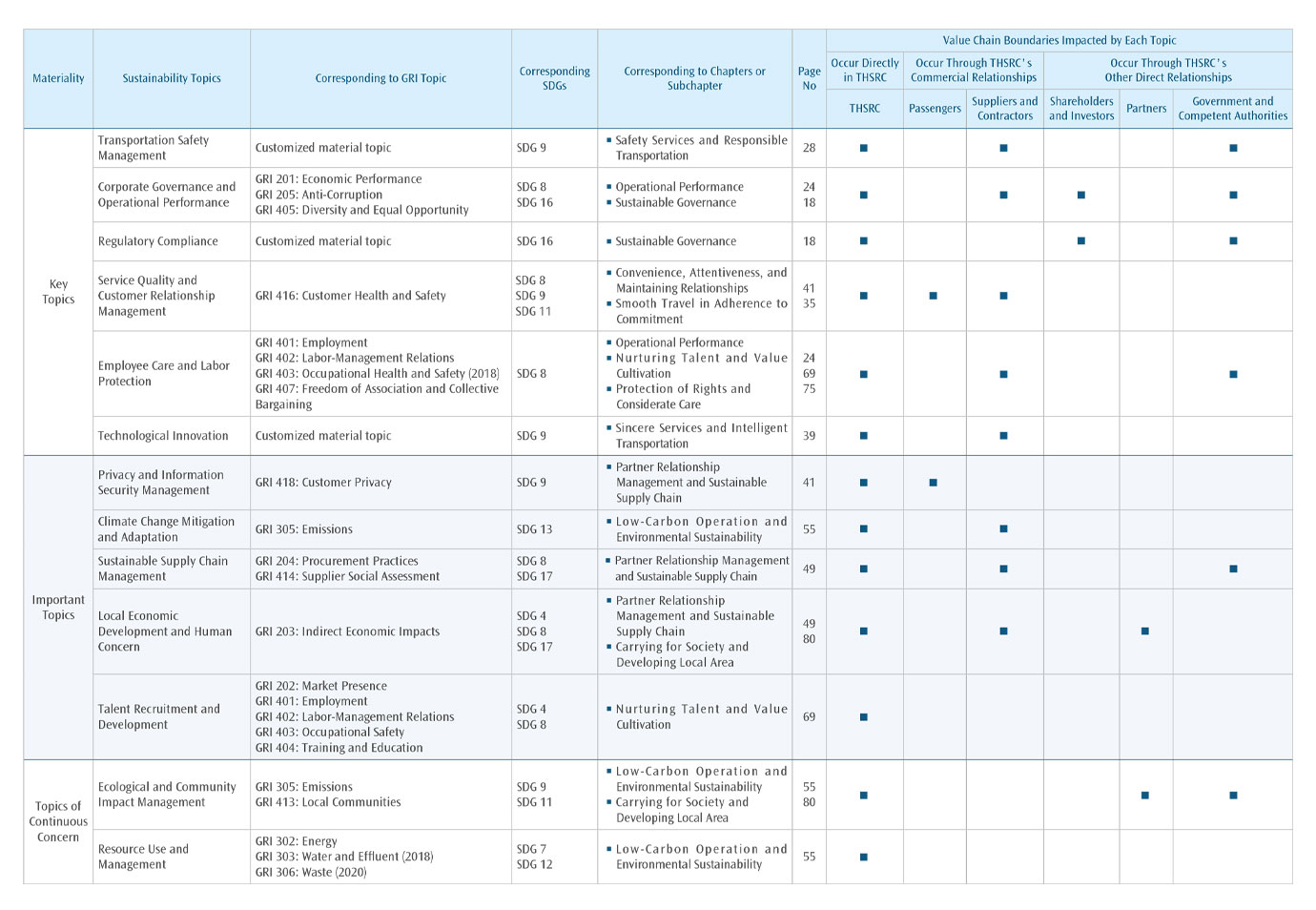
In 2024, THSRC reviewed domestic and international sustainability regulation, ratings, and sustainability topics of benchmark companies to identify the sustainability topics and positive and negative impact issues defined in the previous year and appropriately adjusted the name and impact descriptions of sustainability topics. In addition, the degree of impact and likelihood of occurrence of impacts are adjusted with reference to the due diligence results, and the sustainability topics ranking and materiality matrix of 2024 sustainability report are comprehensively adjusted and completed. Through assess the significance, substantive of the positive and negative impacts of material sustainability topics in terms of economy, environment and human rights, so as to confirm the scope of the report's disclosure and review the effectiveness of sustainable business, and respond to the needs of multiple stakeholders. At the same time, the results of the materiality identification of sustainability topics will be disclosed to the public after being submitted to the Sustainable Development & Nominating Committee and the Board of Directors.
Assessing and Determining Material Sustainability Topics:
| Analysis Steps | Description | Stakeholder and Expert Opinion Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Review the sustainability topics | In order to ensure the sustainability topics keep pace with the times, it also covers the topics of focus of the railway transportation industry. Based on the list of 13 sustainability issues identified in 2023, THSRC refers to the major themes of the railway transportation industry listed by the domestic and foreign regulations and trends and the Sustainable Accounting Standards Board (SASB), the sustainability requirements of international sustainability evaluation such as the Dow Jones Sustainability Index (DJSI), domestic regulations and trends, and the sustainability topics disclosed by international railway transportation benchmarking companies, and reviewed that these 13 sustainability topics are still in line with the industry and global sustainability trends. | External expert sustainability consultants review sustainability topics and advise on how to define the economic, environmental and social impacts of the issues |
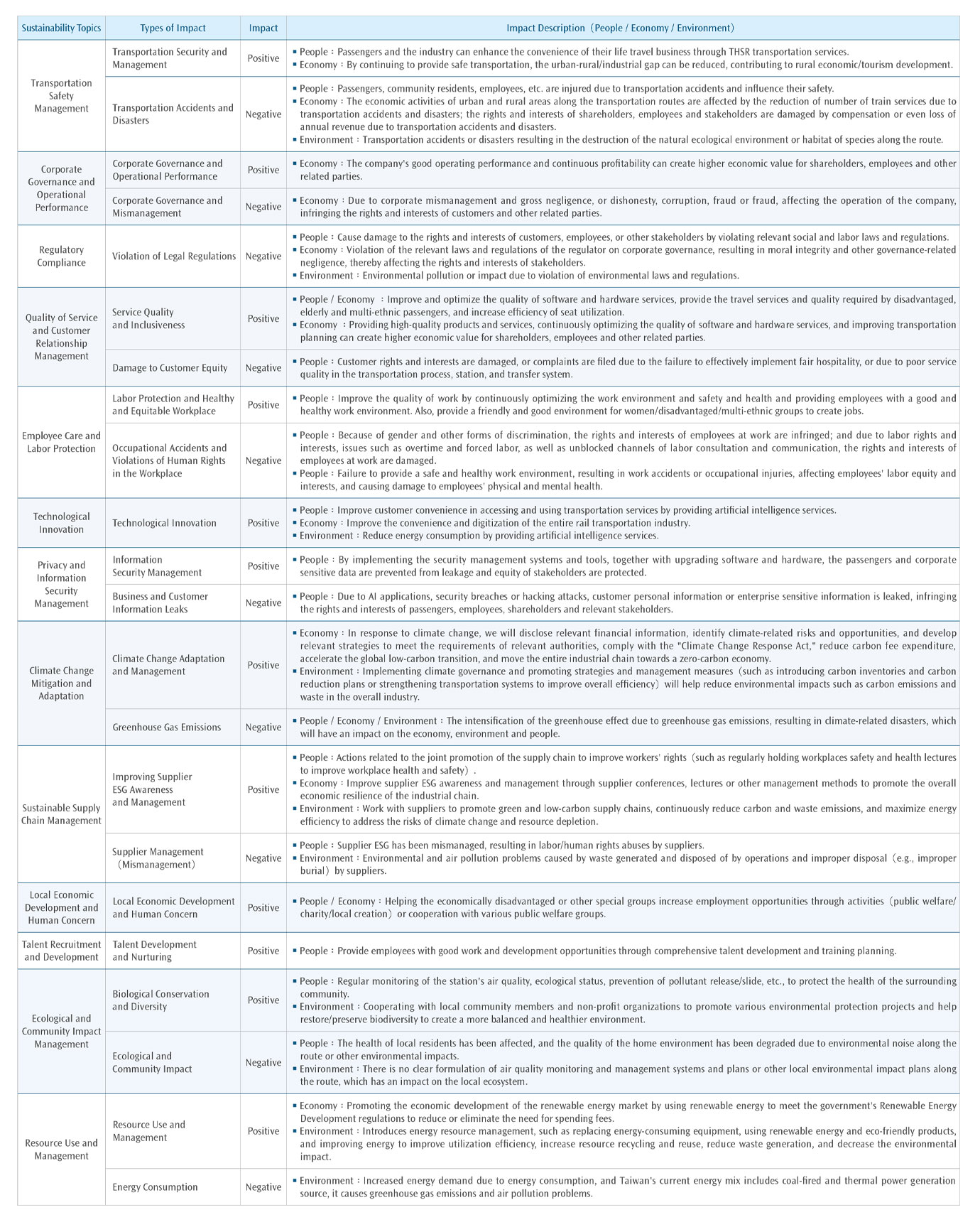
| Evaluate the definition of actual and potential impacts | Re-examine and identify the substance and potential positive and negative impacts of 13 sustainability topics. After re-examination in 2024, the list of 13 topics were re-defined into 12 positive and 10 negative ones and total 22 positive and negative impacts were separately identified. After comprehensive consideration of regulatory trends and industry dynamics, the following adjustments are made: 1. Privacy and Information Security Management ・Negative impact – business and customer information leaks: The increased risk of customer privacy and personal information leakage caused by AI applications was taken into consideration, so the impact description is adjusted to " Due to AI applications, security breaches or hacking attacks, customer personal information or enterprise sensitive information is leaked, infringing the rights and interests of passengers, employees, shareholders and relevant stakeholders." 2. Resource Use and Management ・Positive impact – Resource use and management: Incorporate the concept of recycle and reuse, the impact description has been modified to “Introduces energy resource management, such as replacing energy-consuming equipment, using renewable energy and eco-friendly products, and improving energy to improve utilization efficiency, increase resource recycling and reuse, reduce waste generation, and decrease the environmental impact.” |
|
| Assess and prioritize the most significance of the impacts | Based upon the results of due diligence, THSRC has thoroughly considered the degree of impacts and the likelihood of occurrence of impacts on sustainability topics. In 2024, the following topics were adjusted based upon consideration of the scope of stakeholders affected by the incidents and the likelihood of occurrence: 1. Negative impact - violation of legal regulations: While the number of the penalties has increased compared to 2023, more stakeholder groups were affected. Thus, the degree of impact and the likelihood of occurrence have been adjusted. 2. Negative impact - occupational accidents and violations of human rights in the workplace: Although employee complaints and reports of infringements in 2024 were both decreased compared to 2023, the number of days of disability caused by occupational accidents remained almost the same. Thus, the likelihood of occurrence has been adjusted. |
The significance of sustainability topics is comprehensively assessed and adjusted. Including, but not limited to: ・Travelers: refer to customer satisfaction survey to confirm whether related rights and interests, such as privacy or other customer rights and interests; ・Employees: refer to their opinions and complaints to confirm whether they have been involved in human rights violations in the workplace; ・Suppliers: Refer to their opinions, complaints, and audit results to determine if corporate governance, environmental pollution and labor human rights violations are involved; ・Regulator: Adjust the importance of the issue in light of sustainability and corporate governance relevant assessment or sanctions, as well as policy intentions (such as committing to net-zero emissions by 2050, promoting local manufacturing of the railway transportation industry, local procurement, labor human rights etc.) |
| Adjust and determine material topics for reporting | After completing the assessment, the ranking of material sustainability topics remains the same. In 2024, THSRC remains 6 key topics, 5 important topics, and 2 topics of continuous concern. A total of 13 topics were selected. Among them, "key topics" and "important topics" form the major scope of materiality disclosures in this report. On the other hand, items in “topics of continuous concern” are regarded as non-material topics, where in principle, these items will not be disclosed in this report. However, non-material topics which significantly impact material topics will still be properly explained and disclosed in this report. |
|
| Approval and determine material topics | The results of the materiality analysis of the sustainability topics were submitted to the Sustainability Development & Nomination Committee and the Board of Directors to confirm and approve the key themes of this year's Sustainability Report. Finally, the report will be disclosed to the public. | |
Major analysis results and major thematic matrices
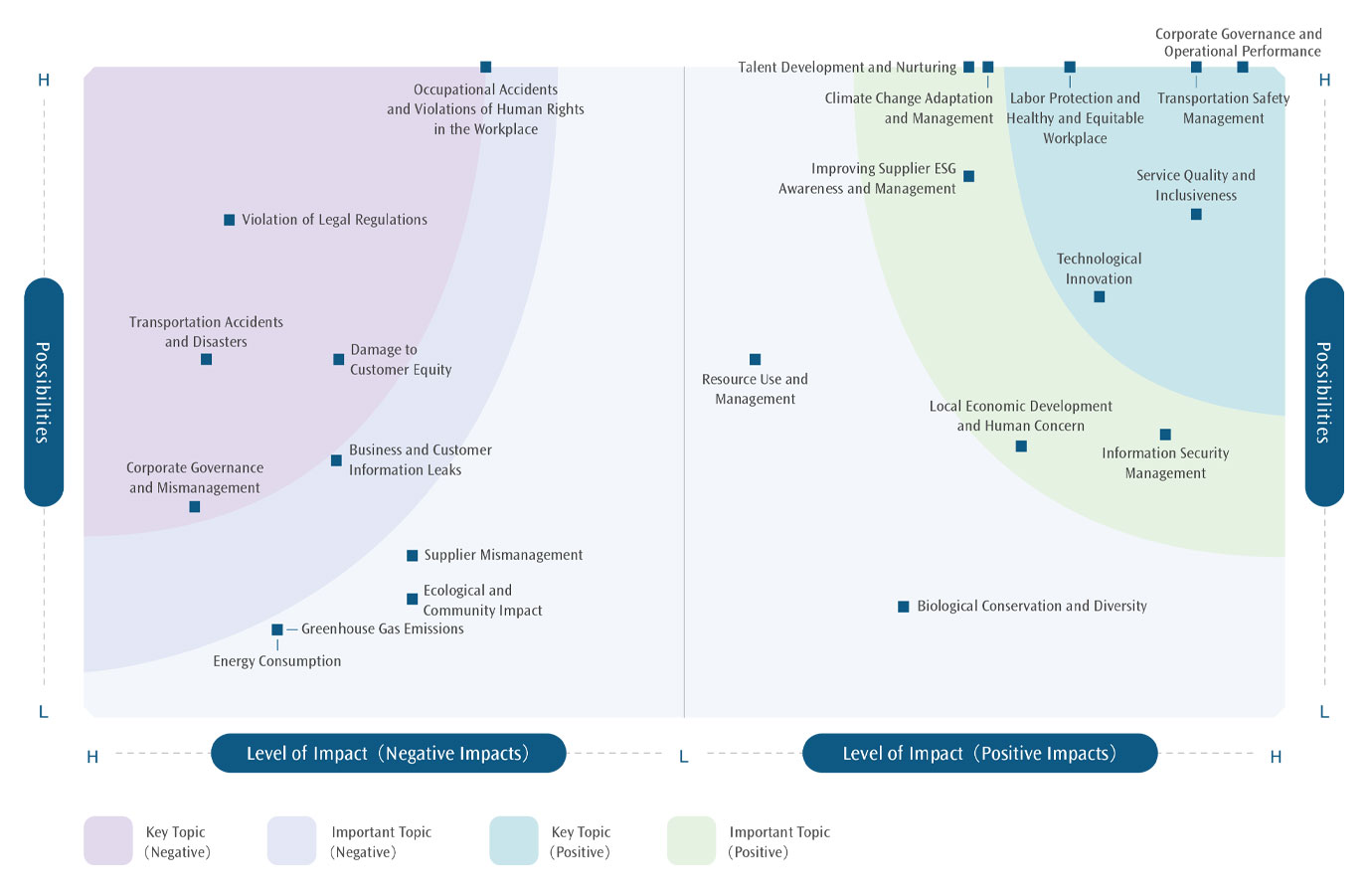
Based on the results of the 2024 assessment, a total of five positive impacts are key issues, five impacts are important issues, and two impacts are rated as ongoing concerns; for negative impacts, a total of five are key issues, three are important issues and two are ongoing concerns. Regardless of whether the topic is positive or negative, as long as one impact is a key topic, the topic will still be identified as a key topic.
In the major theme analysis process, the THSRC has taken suggestions from stakeholders and external experts that the sustainable topics above the material topics(including)should be identified as the topics to be disclosed in this annual report. Compared to the previous year, there is no difference. Thus, in 2024 we remain 6 key topics, 5 important topics and 2 topics of continuous concern, as shown below.
Sustainability Value Chain Impact Management
Materiality Matrix (integration of positive and negative impact)
Note:Negative Impact - Occupational Accidents and Violations of Human Rights in the Workplace: the likelihood of occurrence was already adjusted to the highest level in the matrix in 2023. Therefore, no further adjustments will be made for the current year.